Atorvastatin combined with dexamethasone promote hematoma absorption in an optimized rat model of chronic subdural hematoma
- PMID: 34813498
- PMCID: PMC8660610
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.203717
Atorvastatin combined with dexamethasone promote hematoma absorption in an optimized rat model of chronic subdural hematoma
Abstract
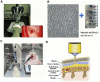
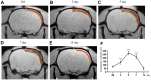
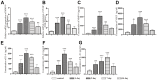
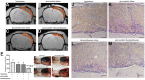
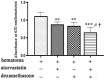
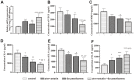
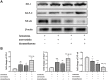
Previous studies found that atorvastatin and dexamethasone were effective in promoting the absorption of chronic subdural hematoma. In this study, we aimed to investigate the effect of pharmacotherapy in an optimized rat model of chronic subdural hematoma. Rat model of chronic subdural hematoma via a bEnd.3 cell and Matrigel mix was established and dynamic changes in different drug treatment groups were tested. The hematoma gradually increased, peaked on the fifth day (263.8±52.85 μl), and was completely absorbed in two weeks. Notably, Kruppelle-like factor 2 expression was significantly decreased with increasing hematoma volume, and then increased in the repair period. The expression of IL-10 was increased and peaked on 7 days, and then decreased at 14 days. The dynamic trends of IL-6, IL-8, MMP-9, and VEGF were also increased first and then decreased. Both monotherapy and the combined treatment by atorvastatin and dexamethasone could counteract the inflammatory activities, decrease hematoma permeability, and improve hematoma absorption, however, most prominent in combined group. The combined treatment could more effectively increase Kruppelle-like factor 2 and ZO-1 expression, attenuate the expression of NF-κb. Most importantly, the combined treatment enhanced the neural functional prognosis and reduced the mortality of chronic subdural hematoma rats. According to our results, the combined treatment could more effectively attenuate inflammatory. And it could also enhance angiogenic activities which could promote the stability of local function and structure of the hematoma cavity, reduce the hematoma volume and improve the outcomes of rats with chronic subdural hematoma than single treatments in the optimized chronic subdural hematoma model.
Keywords: CSDH; angiogenic processes; atorvastatin combined with low-dose dexamethasone treatment; inflammatory activities; optimized CSDH rat model.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
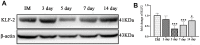

Similar articles
-
Atorvastatin Combined with Low-Dose Dexamethasone Treatment Protects Endothelial Function Impaired by Chronic Subdural Hematoma via the Transcription Factor KLF-2.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020 Aug 12;14:3291-3299. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S256050. eCollection 2020. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020. PMID: 32848367 Free PMC article.
-
Atorvastatin-Induced Absorption of Chronic Subdural Hematoma Is Partially Attributed to the Polarization of Macrophages.J Mol Neurosci. 2022 Mar;72(3):565-573. doi: 10.1007/s12031-021-01910-x. Epub 2021 Sep 26. J Mol Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 34569007
-
Atorvastatin combined with low-dose dexamethasone for vascular endothelial cell dysfunction induced by chronic subdural hematoma.Neural Regen Res. 2021 Mar;16(3):523-530. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.293152. Neural Regen Res. 2021. PMID: 32985481 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of atorvastatin on chronic subdural hematoma: A systematic review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Jun;96(26):e7290. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007290. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28658127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathophysiology and Nonsurgical Treatment of Chronic Subdural Hematoma: From Past to Present to Future.World Neurosurg. 2018 Aug;116:402-411.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2018.05.037. Epub 2018 May 14. World Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 29772364 Review.
Cited by
-
Dexamethasone for delayed edema after intracerebral hemorrhage: To be or not to be?Heliyon. 2023 Jun 28;9(7):e17621. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17621. eCollection 2023 Jul. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37539239 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of Adjuvant Dexamethasone in Chronic Subdural Hematoma After Surgery.Cureus. 2023 Aug 25;15(8):e44086. doi: 10.7759/cureus.44086. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37638268 Free PMC article.
-
The value of computed tomography texture analysis in identifying chronic subdural hematoma patients with a good response to polytherapy.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 12;14(1):3559. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-53376-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38347043 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allison A, Edlmann E, Kolias AG, Davis-Wilkie C, Mee H, Thelin EP, Turner C, Hutchinson PJ, Bond S. Statistical analysis plan for the Dex-CSDH trial: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of a 2-week course of dexamethasone for adult patients with a symptomatic chronic subdural haematoma. Trials. 2019; 20:698. 10.1186/s13063-019-3866-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Miah IP, Holl DC, Peul WC, Walchenbach R, Kruyt N, de Laat K, Koot RW, Volovici V, Dirven CM, van Kooten F, Kho KH, den Hertog HM, van der Naalt J, et al., and Dutch Subdural Hematoma Research Group (DSHR). Dexamethasone therapy versus surgery for chronic subdural haematoma (DECSA trial): study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials. 2018; 19:575. 10.1186/s13063-018-2945-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wang D, Gao C, Xu X, Chen T, Tian Y, Wei H, Zhang S, Quan W, Wang Y, Yue S, Wang Z, Lei P, Anderson C, et al.. Treatment of chronic subdural hematoma with atorvastatin combined with low-dose dexamethasone: phase II randomized proof-of-concept clinical trial. J Neurosurg. 2020. [Epub ahead of print]. 10.3171/2019.11.JNS192020 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

