Close interactions between lncRNAs, lipid metabolism and ferroptosis in cancer
- PMID: 34803512
- PMCID: PMC8579446
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.66181
Close interactions between lncRNAs, lipid metabolism and ferroptosis in cancer
Abstract
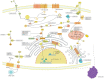
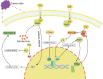
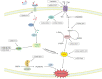
Abnormal lipid metabolism including synthesis, uptake, modification, degradation and transport has been considered a hallmark of malignant tumors and contributes to the supply of substances and energy for rapid cell growth. Meanwhile, abnormal lipid metabolism is also associated with lipid peroxidation, which plays an important role in a newly discovered type of regulated cell death termed ferroptosis. Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been proven to be associated with the occurrence and progression of cancer. Growing evidence indicates that lncRNAs are key regulators of abnormal lipid metabolism and ferroptosis in cancer. In this review, we mainly summarized the mechanism by which lncRNAs regulate aberrant lipid metabolism in cancer, illustrated that lipid metabolism can also influence the expression of lncRNAs, and discussed the mechanism by which lncRNAs affect ferroptosis. A comprehensive understanding of the interactions between lncRNAs, lipid metabolism and ferroptosis could help us to develop novel strategies for precise cancer treatment in the future.
Keywords: Cancer; Ferroptosis; Lipid metabolism; LncRNAs.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long noncoding RNAs induced control of ferroptosis: Implications in cancer progression and treatment.J Cell Physiol. 2023 May;238(5):880-895. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30992. Epub 2023 Mar 16. J Cell Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36924057 Review.
-
LncRNAs regulate metabolism in cancer.Int J Biol Sci. 2020 Feb 10;16(7):1194-1206. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.40769. eCollection 2020. Int J Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32174794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of ferroptosis by non‑coding RNAs in the development and treatment of cancer (Review).Oncol Rep. 2021 Jan;45(1):29-48. doi: 10.3892/or.2020.7836. Epub 2020 Nov 5. Oncol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33155665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Regulation of Ferroptosis by Noncoding RNAs.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 28;24(17):13336. doi: 10.3390/ijms241713336. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37686142 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ferroptosis in Cancer Progression: Role of Noncoding RNAs.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Feb 14;18(5):1829-1843. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.66917. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35342359 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
LncRNA FOXD1-AS1 regulates pancreatic cancer stem cell properties and 5-FU resistance by regulating the miR-570-3p/SPP1 axis as a ceRNA.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Jan 2;24(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-03181-5. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 38167126 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of an immune-related eRNA prognostic signature for clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Jan 29;16(3):2232-2248. doi: 10.18632/aging.205479. Epub 2024 Jan 29. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38289619 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of platelet adhesion-related genes in colon cancer based on non-negative matrix factorization-based clustering algorithm.Digit Health. 2023 Sep 26;9:20552076231203902. doi: 10.1177/20552076231203902. eCollection 2023 Jan-Dec. Digit Health. 2023. PMID: 37766908 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of a novel lipid metabolism-related gene signature to predict outcomes and the tumor immune microenvironment in gastric cancer by integrated analysis of single-cell and bulk RNA sequencing.Lipids Health Dis. 2023 Dec 2;22(1):212. doi: 10.1186/s12944-023-01977-y. Lipids Health Dis. 2023. PMID: 38042786 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive Analysis of a Ferroptosis-Related lncRNA Signature for Predicting Prognosis and Immune Landscape in Osteosarcoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 28;12:880459. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.880459. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35837104 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abramson HN. The lipogenesis pathway as a cancer target. J Med Chem. 2011;54(16):5615–5638. - PubMed
-
- Santos CR, Schulze A. Lipid metabolism in cancer. FEBS J. 2012;279(15):2610–2623. - PubMed
-
- Pomorski T, Hrafnsdottir S, Devaux PF, van Meer G. Lipid distribution and transport across cellular membranes. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2001;12(2):139–148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

