Electroacupuncture Plus Auricular Acupressure on Chemotherapy-Related Insomnia in Patients With Breast Cancer (EACRI): Study Protocol for a Randomized, Sham-Controlled Trial
- PMID: 34802291
- PMCID: PMC8606933
- DOI: 10.1177/15347354211058695
Electroacupuncture Plus Auricular Acupressure on Chemotherapy-Related Insomnia in Patients With Breast Cancer (EACRI): Study Protocol for a Randomized, Sham-Controlled Trial
Abstract
Objective: Insomnia is a highly prevalent and disturbing symptom in breast cancer patients under or post chemotherapy. If not appropriately treated, it can persist for years after the completion of cancer treatments. Acupuncture has been widely used for alleviating insomnia. The aim of this study is to examine the feasibility, efficacy and safety of acupuncture for chemotherapy-related insomnia among patients with breast cancer.
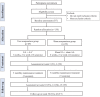
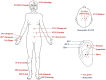
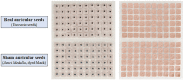
Materials and methods: This is a trial protocol for a randomized, sham-controlled, subject- and assessor-blinded clinical trial. A total of 138 eligible participants will be assigned randomly to acupuncture or sham control group at a ratio of 1:1. Participants in acupuncture group will receive electroacupuncture (EA) plus auricular acupressure (AA) treatment, while subjects in sham acupuncture group will receive sham EA plus sham AA. Both acupuncture and sham treatments will be given twice weekly for 6 weeks, followed by maintenance treatments once every 4 weeks for 12 weeks (15 sessions totally). The primary outcome is the change of Insomnia Severity Index score between baseline and the end of 6-week treatment. Secondary outcome measurements include Actiwatch, sleep diary, Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index, Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy-Breast Cancer, Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale, Brief Pain Inventory-Short Form, Brief Fatigue Inventory, Acupuncture Expectancy Scale, credibility, and adverse events. Participants will be followed up to 42 weeks.
Conclusions: This trial will expand our understanding of the feasibility, efficacy, and safety of acupuncture as a treatment for alleviating chemotherapy-related insomnia in patients with breast cancer. EA plus AA, if proven to be effective, can be implemented into routine settings to play a role in insomnia management for patients with breast cancer.
Keywords: auricular acupressure; breast cancer; chemotherapy; electroacupuncture; insomnia; sham control.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acupuncture for chemotherapy-associated insomnia in breast cancer patients: an assessor-participant blinded, randomized, sham-controlled trial.Breast Cancer Res. 2023 Apr 26;25(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s13058-023-01645-0. Breast Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37101228 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Electroacupuncture Plus Auricular Acupressure for Chemotherapy-Associated Insomnia in Breast Cancer Patients: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial.Integr Cancer Ther. 2021 Jan-Dec;20:15347354211019103. doi: 10.1177/15347354211019103. Integr Cancer Ther. 2021. PMID: 34036813 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of acupuncture versus sham/placebo acupuncture for insomnia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2020 Nov;41:101253. doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2020.101253. Epub 2020 Nov 1. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2020. PMID: 33186824
-
Acupuncture for insomnia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jul 18;(3):CD005472. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005472.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Sep 12;(9):CD005472. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005472.pub3. PMID: 17636800 Updated. Review.
-
Acupuncture for insomnia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Sep 12;2012(9):CD005472. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005472.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 22972087 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Research trends of acupressure from 2004 to 2024: A bibliometric and visualization analysis.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 29;10(21):e38675. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38675. eCollection 2024 Nov 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39568827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Are Published Cancer Care Trial Protocols With Traditional Chinese Medicine Interventions Concordant With SPIRIT-TCM Extension 2018? A Scoping Review on Published Trial Protocols Between 2019 and 2022.Integr Cancer Ther. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15347354231223966. doi: 10.1177/15347354231223966. Integr Cancer Ther. 2024. PMID: 38291957 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture for chemotherapy-associated insomnia in breast cancer patients: an assessor-participant blinded, randomized, sham-controlled trial.Breast Cancer Res. 2023 Apr 26;25(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s13058-023-01645-0. Breast Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37101228 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Role of Chinese Acupuncture in the Treatment for Chemotherapy-Induced Cognitive Impairment in Older Patients With Cancer: Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial.JMIR Res Protoc. 2024 Feb 8;13:e53853. doi: 10.2196/53853. JMIR Res Protoc. 2024. PMID: 38329790 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Pub. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5®). American Psychiatric Pub; 2013.
-
- Delgado-Guay M, Yennurajalingam S, Parsons H, Palmer JL, Bruera E. Association between self-reported sleep disturbance and other symptoms in patients with advanced cancer. J Pain Symptom Manag. 2011;41:819-827. - PubMed
-
- Cheng KK, Yeung RM. Impact of mood disturbance, sleep disturbance, fatigue and pain among patients receiving cancer therapy. Eur J Cancer Care. 2013;22:70-78. - PubMed
-
- Savard J, Ivers H, Villa J, Caplette-Gingras A, Morin CM. Natural course of insomnia comorbid with cancer: an 18-month longitudinal study. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:3580-3586. - PubMed
-
- Savard J, Ivers H, Savard MH, Morin CM. Cancer treatments and their side effects are associated with aggravation of insomnia: results of a longitudinal study. Cancer. 2015;121:1703-1711. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical