Clinical Effects of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine in Treating Severe Preeclampsia and Its Influence on Maternal and Infant Outcomes after Cesarean Section under Combined Lumbar and Epidural Anesthesia
- PMID: 34790247
- PMCID: PMC8592741
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6366914
Clinical Effects of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine in Treating Severe Preeclampsia and Its Influence on Maternal and Infant Outcomes after Cesarean Section under Combined Lumbar and Epidural Anesthesia
Abstract
Objective: This study is aimed to observe the clinical effects of integrated traditional Chinese and Western medicine in treating severe preeclampsia (SPE) and its effects on maternal and infant outcomes after cesarean section under combined lumbar and epidural anesthesia.
Method: One hundred and sixty-six pregnant women with SPE were randomly divided into an experimental group and control group, with 83 cases in each group. The control group was given conventional treatments such as magnesium sulfate, and the experimental group received self-made traditional Chinese medicine decoction for oral administration.
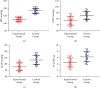
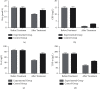
Results: The total clinical effective rate of treatment in the experimental group was significantly higher than that in the control group. After treatment, the systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), mean arterial pressure (MAP), and 24 h proteinuria (24 h PRO) levels of the experimental group were significantly lower than those of the control group. After cesarean section (c-section) under combined lumbar and epidural anesthesia, there were statistically significant differences in placental abruption, uterine weakness, fetal intrauterine distress, and neonatal asphyxia in the experimental group, while there were no significant differences in oligohydramnios. After treatment, the contents of inflammatory factors in both groups decreased, and the decrease was more prominent in the experimental group. After treatment, the levels of blood urea nitrogen (BUN), serum creatinine (Scr), and albumin (Alb) and β2 microglobulin (β2-MG) of the two groups of patients decreased, and the levels of them in the experimental group decreased. After treatment, the levels of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) in the two groups increased. However, the levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), lipid peroxide (LPO), and advanced oxidation protein products (AOPP) all reduced, and the increase or decrease in the experimental group was more prominent.
Conclusion: The combination of traditional Chinese and Western medicine can reduce the blood pressure of a patient with SPE. After the combined spinal-epidural anesthesia and cesarean section, it can significantly improve the maternal and infant outcomes and renal function, reduce inflammatory factors levels and body oxidative stress, and increase the activities of antioxidant enzymes.
Copyright © 2021 Xiaolu Wang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Effects of double-catheter epidural analgesia by lidocaine injection respectively on the delivery outcomes and maternal-infant complications for persistent posterior or lateral occipital position of protracted active phase].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2020 Jul 25;55(7):457-464. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112141-20191228-00705. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32842249 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Effect of Combined Spinal-Epidural Anesthesia and Total Intravenous Anesthesia on Hemodynamics and Pregnancy Outcomes of Severe Preeclampsia Pregnant Patients Undergoing Cesarean Section.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Feb 22;2022:2655858. doi: 10.1155/2022/2655858. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. Retraction in: Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Jul 19;2023:9754758. doi: 10.1155/2023/9754758 PMID: 35242197 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
[Study of coenzyme Q10 in the liver of preeclampsia pregnant rats].Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2016 Aug 25;51(8):608-15. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-567X.2016.08.011. Zhonghua Fu Chan Ke Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 27561941 Chinese.
-
Combined spinal and epidural anesthesia with low doses of intrathecal bupivacaine in women with severe preeclampsia: a preliminary report.Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2001 Jan-Feb;26(1):46-51. doi: 10.1053/rapm.2001.18182. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2001. PMID: 11172511 Clinical Trial.
-
Appropriate Method of Administering Vasopressors for Maternal Hypotension Associated with Combined Spinal Epidural Anesthesia in Elective Cesarean Section: Impact on Postnatal Respiratory Support for Newborns.Medicina (Kaunas). 2022 Mar 8;58(3):403. doi: 10.3390/medicina58030403. Medicina (Kaunas). 2022. PMID: 35334579 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chou M. H., Huang H. H., Lai Y. J. Cardiac arrest during emergency cesarean section for severe pre-eclampsia and peripartum cardiomyopathy. Taiwanese Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology . 2016;55(1):125–127. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

