miR-21 in Human Cardiomyopathies
- PMID: 34778418
- PMCID: PMC8578278
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.767064
miR-21 in Human Cardiomyopathies
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: miR-21 in Human Cardiomyopathies.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Apr 25;9:913429. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.913429. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35548429 Free PMC article.
Abstract
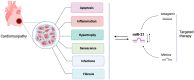
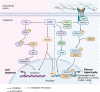
miR-21 is a 22-nucleotide long microRNA that matches target mRNAs in a complementary base pairing fashion and regulates gene expression by repressing or degrading target mRNAs. miR-21 is involved in various cardiomyopathies, including heart failure, dilated cardiomyopathy, myocardial infarction, and diabetic cardiomyopathy. Expression levels of miR-21 notably change in both heart and circulation and provide cardiac protection after heart injury. In the meantime, miR-21 also tightly links to cardiac dysfunctions such as cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis. This review focuses on the miR-21 expression pattern and its functions in diseased-heart and further discusses the feasibility of miR-21 as a biomarker and therapeutic target in cardiomyopathies.
Keywords: biomarkers; cardiomyopathies; fibrosis; miR-21; targeted therapy.
Copyright © 2021 Surina, Fontanella, Scisciola, Marfella, Paolisso and Barbieri.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA targets and biomarker validation for diabetes-associated cardiac fibrosis.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Dec;174:105941. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105941. Epub 2021 Oct 14. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 34656765 Review.
-
Direct and indirect involvement of microRNA-499 in clinical and experimental cardiomyopathy.Circ Res. 2012 Aug 17;111(5):521-31. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.265736. Epub 2012 Jun 29. Circ Res. 2012. PMID: 22752967 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs as Biomarkers in Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: Current State of the Art.Curr Med Chem. 2021;28(36):7400-7412. doi: 10.2174/0929867328666210405122703. Curr Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33820510 Review.
-
Sex differences in response to miRNA-34a therapy in mouse models of cardiac disease: identification of sex-, disease- and treatment-regulated miRNAs.J Physiol. 2016 Oct 15;594(20):5959-5974. doi: 10.1113/JP272512. Epub 2016 Jul 20. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27270487 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-30d regulates cardiomyocyte pyroptosis by directly targeting foxo3a in diabetic cardiomyopathy.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Oct 23;5(10):e1479. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.430. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 25341033 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
RNA-Based Liquid Biopsy in Head and Neck Cancer.Cells. 2023 Jul 23;12(14):1916. doi: 10.3390/cells12141916. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37508579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiR-21-3p inhibitor exerts myocardial protective effects by altering macrophage polarization state and reducing excessive mitophagy.Commun Biol. 2024 Oct 22;7(1):1371. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-07050-3. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39438580 Free PMC article.
-
The roles and mechanisms of epigenetic regulation in pathological myocardial remodeling.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Aug 26;9:952949. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.952949. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36093141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of non-coding RNA in diabetic cardiomyopathy.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Jun 29;23(1):227. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02252-9. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 38951895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances on the Molecular Mechanism and Clinical Trials of Venous Thromboembolism.J Inflamm Res. 2023 Dec 14;16:6167-6178. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S439205. eCollection 2023. J Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 38111686 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhang Y, Liu YJ, Liu T, Zhang H, Yang SJ. Plasma microRNA-21 is a potential diagnostic biomarker of acute myocardial infarction. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2016)20:323–9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

