Silmitasertib-induced macropinocytosis promoting DDP intracellular uptake to enhance cell apoptosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 34766543
- PMCID: PMC8592591
- DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2021.2000677
Silmitasertib-induced macropinocytosis promoting DDP intracellular uptake to enhance cell apoptosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
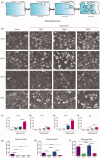
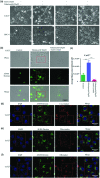
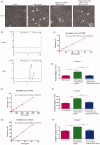
Cisplatin (DDP) is a first-line chemotherapeutic drug applied for the treatment of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). The anticancer activity of DDP is tightly linked to its intracellular uptake. It is unwise to increase the DDP intake by increasing the dose or shortening the dosing interval because of the severe systemic toxicity (nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity and neurotoxicity) in DDP application. The main uptake pathways of DDP include passive diffusion and active transporter transport. Therefore, finding additional uptake pathways that can improve the effective intracellular concentration of DDP is critical. Macropinocytosis, an endocytic mechanism for extracellular material absorption, contributes to the intracellular uptake of anticancer drugs. No research has been conducted to determine whether macropinocytosis can augment the intracellular uptake of DDP in OSCC cells or not. Based on that, we proved for the first time that silmitasertib (previously CX-4945) could trigger macropinocytosis, which may increase the intracellular uptake of DDP and enhance apoptosis via in vivo and in vitro experiments. We hope that our findings will inspire a new approach for the application of DDP in cancer treatment.
Keywords: Oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC); apoptosis; cisplatin (DDP) intracellular uptake; macropinocytosis; silmitasertib.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CX-4945 (Silmitasertib) Induces Cell Death by Impairing Lysosomal Utilization in KRAS Mutant Cholangiocarcinoma Cell Lines.Anticancer Res. 2024 May;44(5):1939-1946. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.16996. Anticancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38677763
-
LncRNA UCA1 promotes proliferation and cisplatin resistance of oral squamous cell carcinoma by sunppressing miR-184 expression.Cancer Med. 2017 Dec;6(12):2897-2908. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1253. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Cancer Med. 2017. PMID: 29125238 Free PMC article.
-
MS-275 combined with cisplatin exerts synergistic antitumor effects in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020 May 15;395:114971. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2020.114971. Epub 2020 Mar 23. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32217144
-
Targeted drug delivery system inspired by macropinocytosis.J Control Release. 2023 Jul;359:302-314. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.06.011. Epub 2023 Jun 14. J Control Release. 2023. PMID: 37307923 Review.
-
Atypical Macropinocytosis Contributes to Malignant Progression: A Review of Recent Evidence in Endometrioid Endometrial Cancer Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 15;14(20):5056. doi: 10.3390/cancers14205056. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36291839 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cellular Regulation of Macropinocytosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 26;25(13):6963. doi: 10.3390/ijms25136963. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role and Therapeutic Potential of Macropinocytosis in Cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 15;13:919819. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.919819. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36046825 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Belaid A, Filippakis H. (2021). Quantitative assessment of macropinocytosis in mTORC1-hyperactive cells using flow cytometry. J Vis Exp 2:174. - PubMed
-
- Chen F, Pei S, Wang X, et al. (2020). Emerging JWA-targeted Pt (IV) prodrugs conjugated with CX-4945 to overcome chemo-immune-resistance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 521:753–61. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
