Roles of calcitonin gene-related peptide in the skin, and other physiological and pathophysiological functions
- PMID: 34746878
- PMCID: PMC8551410
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbih.2021.100361
Roles of calcitonin gene-related peptide in the skin, and other physiological and pathophysiological functions
Abstract
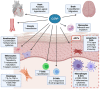
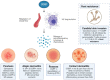
Skin immunity is regulated by many mediator molecules. One is the neuropeptide calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP). CGRP has roles in regulating the function of components of the immune system including T cells, B cells, dendritic cells (DCs), endothelial cells (ECs), and mast cells (MCs). Herein we discuss actions of CGRP in mediating inflammatory and vascular effects in various cutaneous models and disorders.
Keywords: CGRP; Calcitonin gene-related peptide; Cutaneous disorders; Immunoregulation; Neurogenic inflammation; Skin immunity; Therapeutic target.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
RDG is on the scientific advisory boards of Elysium Health and Hoth Therapeutics. He is also on the Industry Advisory Board of Gore Range Capital and has research agreements with Leo Pharma, the Leo Foundation, Galderma, Pfizer and Elysium Health.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neuromediators--a crucial component of the skin immune system.J Dermatol Sci. 2002 Nov;30(2):87-93. doi: 10.1016/s0923-1811(02)00103-2. J Dermatol Sci. 2002. PMID: 12413763
-
Calcitonin gene-related peptide: key regulator of cutaneous immunity.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2015 Mar;213(3):586-94. doi: 10.1111/apha.12442. Epub 2015 Jan 5. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2015. PMID: 25534428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Regulatory mechanisms of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) in skin inflammation].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2012;132(11):1211-5. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.12-00232-1. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2012. PMID: 23123709 Review. Japanese.
-
Calcitonin gene-related peptide is an important regulator of cutaneous immunity: effect on dendritic cell and T cell functions.J Immunol. 2011 Jun 15;186(12):6886-93. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1100028. Epub 2011 May 6. J Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21551361
-
Calcitonin gene-related peptide decreases expression of HLA-DR and CD86 by human dendritic cells and dampens dendritic cell-driven T cell-proliferative responses via the type I calcitonin gene-related peptide receptor.J Immunol. 2000 Apr 1;164(7):3494-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.7.3494. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10725702
Cited by
-
Changes of Endothelin-1 and Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Concentrations in Patients with Cervical Radiculopathy after Wrist-Ankle Acupuncture-Moxibustion and Hot Compression with Chinese Herbal Medicine.Genet Res (Camb). 2021 Dec 18;2021:5433742. doi: 10.1155/2021/5433742. eCollection 2021. Genet Res (Camb). 2021. PMID: 35002538 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Human Mast Cells Upregulate Cathepsin B, a Novel Marker of Itch in Psoriasis.Cells. 2023 Aug 30;12(17):2177. doi: 10.3390/cells12172177. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37681909 Free PMC article.
-
Fc Epsilon RI-Neuroimmune Interplay in Pruritus Triggered by Particulate Matter in Atopic Dermatitis Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 24;24(14):11851. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411851. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511610 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroimmune interactions in atopic and allergic contact dermatitis.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023 May;151(5):1169-1177. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2023.03.013. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37149370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Medical Therapies in Rosacea: A Narrative Review.Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023 Dec;13(12):2933-2949. doi: 10.1007/s13555-023-01048-1. Epub 2023 Oct 12. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2023. PMID: 37824060 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdel-Malek Z.A. Endocrine factors as effectors of integumental pigmentation. Dermatol. Clin. 1988;6(2):175–183. - PubMed
-
- Akaishi S., Ogawa R., Hyakusoku H. Keloid and hypertrophic scar: neurogenic inflammation hypotheses. Med. Hypotheses. 2008;71(1):32–38. - PubMed
-
- Albertin G., Carraro G., Parnigotto P.P., Conconi M.T., Ziolkowska A., Malendowicz L.K., Nussdorfer G.G. Human skin keratinocytes and fibroblasts express adrenomedullin and its receptors, and adrenomedullin enhances their growth in vitro by stimulating proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2003;11(5):635–639. - PubMed
-
- Alevizaki M., Shiraishi A., Rassool F.V., Ferrier G.J., MacIntyre I., Legon S. The calcitonin-like sequence of the beta CGRP gene. FEBS Lett. 1986;206(1):47–52. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

