Signal processing capacity of the cellular sensory machinery regulates the accuracy of chemotaxis under complex cues
- PMID: 34746705
- PMCID: PMC8554535
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103242
Signal processing capacity of the cellular sensory machinery regulates the accuracy of chemotaxis under complex cues
Abstract
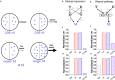
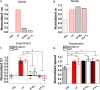
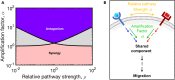
Chemotaxis is ubiquitous in many biological processes, but it still remains elusive how cells sense and decipher multiple chemical cues. In this study, we postulate a hypothesis that the chemotactic performance of cells under complex cues is regulated by the signal processing capacity of the cellular sensory machinery. The underlying rationale is that cells in vivo should be able to sense and process multiple chemical cues, whose magnitude and compositions are entangled, to determine their migration direction. We experimentally show that the combination of transforming growth factor-β and epidermal growth factor suppresses the chemotactic performance of cancer cells using independent receptors to sense the two cues. Based on this observation, we develop a biophysical framework suggesting that the antagonism is caused by the saturation of the signal processing capacity but not by the mutual repression. Our framework suggests the significance of the signal processing capacity in the cellular sensory machinery.
Keywords: Cell biology; Mathematical biosciences; Systems biology.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cells function as a ternary logic gate to decide migration direction under integrated chemical and fluidic cues.Lab Chip. 2023 Feb 14;23(4):631-644. doi: 10.1039/d2lc00807f. Lab Chip. 2023. PMID: 36524874 Free PMC article.
-
Information processing in bacteria: memory, computation, and statistical physics: a key issues review.Rep Prog Phys. 2016 May;79(5):052601. doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/79/5/052601. Epub 2016 Apr 8. Rep Prog Phys. 2016. PMID: 27058315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cells use molecular working memory to navigate in changing chemoattractant fields.Elife. 2022 Jun 6;11:e76825. doi: 10.7554/eLife.76825. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35666122 Free PMC article.
-
Development and applications of a model for cellular response to multiple chemotactic cues.J Math Biol. 2000 Oct;41(4):285-314. doi: 10.1007/s002850000035. J Math Biol. 2000. PMID: 11103868
-
Decoding the chemotactic signal.J Leukoc Biol. 2018 Aug;104(2):359-374. doi: 10.1002/JLB.1MR0218-044. Epub 2018 Jun 6. J Leukoc Biol. 2018. PMID: 29873835 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deduction of signaling mechanisms from cellular responses to multiple cues.NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2022 Nov 30;8(1):48. doi: 10.1038/s41540-022-00262-5. NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2022. PMID: 36450797 Free PMC article.
-
Cells function as a ternary logic gate to decide migration direction under integrated chemical and fluidic cues.Lab Chip. 2023 Feb 14;23(4):631-644. doi: 10.1039/d2lc00807f. Lab Chip. 2023. PMID: 36524874 Free PMC article.
-
The ability to sense the environment is heterogeneously distributed in cell populations.Elife. 2024 Jan 31;12:RP87747. doi: 10.7554/eLife.87747. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38293960 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alon U., Surette M.G., Barkai N., Leibler S. Robustness in bacterial chemotaxis. Nature. 1999;397:168–171. - PubMed
-
- Carballo-Pacheco M., Desponds J., Gavrilchenko T., Mayer A., Prizak R., Reddy G., Nemenman I., Mora T. Receptor crosstalk improves concentration sensing of multiple ligands. Phys. Rev. E. 2019;99:022423. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

