Human Sirtuin Regulators: The "Success" Stories
- PMID: 34744791
- PMCID: PMC8568457
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2021.752117
Human Sirtuin Regulators: The "Success" Stories
Abstract
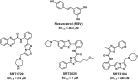
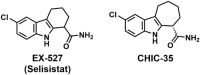
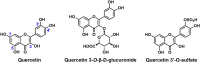
The human sirtuins are a group of NAD+-dependent protein deacylases. They "erase" acyl modifications from lysine residues in various cellular targets including histones, transcription factors, and metabolic enzymes. Through these far-reaching activities, sirtuins regulate a diverse array of biological processes ranging from gene transcription to energy metabolism. Human sirtuins have been intensely pursued by both academia and industry as therapeutic targets for a broad spectrum of diseases such as cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and metabolic disorders. The last two decades have witnessed a flood of small molecule sirtuin regulators. However, there remain relatively few compounds targeting human sirtuins in clinical development. This reflects the inherent issues concerning the development of isoform-selective and potent molecules with good drug-like properties. In this article, small molecule sirtuin regulators that have advanced into clinical trials will be discussed in details as "successful" examples for future drug development. Special attention is given to the discovery of these compounds, the mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics analysis, formulation, as well as the clinical outcomes observed in the trials.
Keywords: activator; clinical trial; drug development; inhibitor; sirtuin.
Copyright © 2021 Curry, White, Donu and Cen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Current Trends in Sirtuin Activator and Inhibitor Development.Molecules. 2024 Mar 6;29(5):1185. doi: 10.3390/molecules29051185. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38474697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New assays and approaches for discovery and design of Sirtuin modulators.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2014 Feb;9(2):183-99. doi: 10.1517/17460441.2014.875526. Epub 2014 Jan 2. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2014. PMID: 24382304 Review.
-
Biology, Chemistry, and Pharmacology of Sirtuins.Methods Enzymol. 2016;574:183-211. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2016.03.011. Epub 2016 Mar 28. Methods Enzymol. 2016. PMID: 27423863
-
Activation and inhibition of sirtuins: From bench to bedside.Med Res Rev. 2024 Aug 31. doi: 10.1002/med.22076. Online ahead of print. Med Res Rev. 2024. PMID: 39215785 Review.
-
Structures, substrates, and regulators of Mammalian sirtuins - opportunities and challenges for drug development.Front Pharmacol. 2012 Feb 9;3:16. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2012.00016. eCollection 2012. Front Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22363286 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Challenges in Pharmacological Intervention in Perilipins (PLINs) to Modulate Lipid Droplet Dynamics in Obesity and Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Aug 7;15(15):4013. doi: 10.3390/cancers15154013. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37568828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Multi-Faceted Role of Sirtuins in Glioblastoma Pathogenesis and Targeting Options.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 25;23(21):12889. doi: 10.3390/ijms232112889. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36361680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of sirtuins in esophageal cancer: Current status and future prospects.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022 Apr 15;14(4):794-807. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v14.i4.794. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35582109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging therapies for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease with a focus on cAMP signaling.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Sep 2;9:981963. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.981963. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36120538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effects of Nutrient Signaling Regulators in Combination with Phytocannabinoids on the Senescence-Associated Phenotype in Human Dermal Fibroblasts.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 8;23(15):8804. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158804. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955938 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aftanas L. I., Markov A. A., Rikita M. V., Danilenko K. V. (2020). P.326 Efficacy of resveratrol in the treatment of unipolar depression: double-blind randomized placebo-controlled parallel-group study. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 40:S189.
-
- Agarwal B., Campen M. J., Channell M. M., Wherry S. J., Varamini B., Davis J. G., et al. (2013). Resveratrol for primary prevention of atherosclerosis: clinical trial evidence for improved gene expression in vascular endothelium. Int. J. Cardiol. 166 246–248. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2012.09.027 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources