A reactive center loop-based prediction platform to enhance the design of therapeutic SERPINs
- PMID: 34740972
- PMCID: PMC8609344
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2108458118
A reactive center loop-based prediction platform to enhance the design of therapeutic SERPINs
Abstract
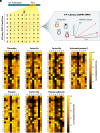
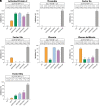
Serine proteases are essential for many physiological processes and require tight regulation by serine protease inhibitors (SERPINs). A disturbed SERPIN-protease balance may result in disease. The reactive center loop (RCL) contains an enzymatic cleavage site between the P1 through P1' residues that controls SERPIN specificity. This RCL can be modified to improve SERPIN function; however, a lack of insight into sequence-function relationships limits SERPIN development. This is complicated by more than 25 billion mutants needed to screen the entire P4 to P4' region. Here, we developed a platform to predict the effects of RCL mutagenesis by using α1-antitrypsin as a model SERPIN. We generated variants for each of the residues in P4 to P4' region, mutating them into each of the 20 naturally occurring amino acids. Subsequently, we profiled the reactivity of the resulting 160 variants against seven proteases involved in coagulation. These profiles formed the basis of an in silico prediction platform for SERPIN inhibitory behavior with combined P4 to P4' RCL mutations, which were validated experimentally. This prediction platform accurately predicted SERPIN behavior against five out of the seven screened proteases, one of which was activated protein C (APC). Using these findings, a next-generation APC-inhibiting α1-antitrypsin variant was designed (KMPR/RIRA; / indicates the cleavage site). This variant attenuates blood loss in an in vivo hemophilia A model at a lower dosage than the previously developed variant AIKR/KIPP because of improved potency and specificity. We propose that this SERPIN-based RCL mutagenesis approach improves our understanding of SERPIN behavior and will facilitate the design of therapeutic SERPINs.
Keywords: SERPIN; hemophilia; protein engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identification of serpin determinants of specificity and selectivity for furin inhibition through studies of α1PDX (α1-protease inhibitor Portland)-serpin B8 and furin active-site loop chimeras.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jul 26;288(30):21802-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.462804. Epub 2013 Jun 6. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23744066 Free PMC article.
-
Importance of the P4' residue in human granzyme B inhibitors and substrates revealed by scanning mutagenesis of the proteinase inhibitor 9 reactive center loop.J Biol Chem. 2001 May 4;276(18):15177-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M006645200. Epub 2001 Feb 1. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11278311
-
Viral Serpin Reactive Center Loop (RCL) Peptides: Design and Testing.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1826:133-142. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-8645-3_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 30194598
-
Therapeutic SERPINs: Improving on Nature.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Mar 31;8:648349. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.648349. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 33869308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering the serpin α1 -antitrypsin: A diversity of goals and techniques.Protein Sci. 2020 Apr;29(4):856-871. doi: 10.1002/pro.3794. Epub 2019 Dec 9. Protein Sci. 2020. PMID: 31774589 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Parasitoid Serpins Evolve Novel Functions to Manipulate Host Homeostasis.Mol Biol Evol. 2023 Dec 1;40(12):msad269. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msad269. Mol Biol Evol. 2023. PMID: 38061001 Free PMC article.
-
The Crystal Structure of the Michaelis-Menten Complex of C1 Esterase Inhibitor and C1s Reveals Novel Insights into Complement Regulation.J Immunol. 2024 Sep 1;213(5):718-729. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2400194. J Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38995166
-
Anticoagulant SERPINs: Endogenous Regulators of Hemostasis and Thrombosis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 May 3;9:878199. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.878199. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35592395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hemophilia a patients with inhibitors: Mechanistic insights and novel therapeutic implications.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 8;13:1019275. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1019275. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36569839 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hedstrom L., Serine protease mechanism and specificity. Chem. Rev. 102, 4501–4524 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Loebermann H., Tokuoka R., Deisenhofer J., Huber R., Human α 1-proteinase inhibitor. Crystal structure analysis of two crystal modifications, molecular model and preliminary analysis of the implications for function. J. Mol. Biol. 177, 531–557 (1984). - PubMed
-
- Huntington J. A., Read R. J., Carrell R. W., Structure of a serpin-protease complex shows inhibition by deformation. Nature 407, 923–926 (2000). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

