The Impact of Environmental Pollutants on Barrier Dysfunction in Respiratory Disease
- PMID: 34734504
- PMCID: PMC8569032
- DOI: 10.4168/aair.2021.13.6.850
The Impact of Environmental Pollutants on Barrier Dysfunction in Respiratory Disease
Abstract
Respiratory epithelial cells form a selective barrier between the outside environment and underlying tissues. Epithelial cells are polarized and form specialized cell-cell junctions, known as the apical junctional complex (AJC). Assembly and disassembly of the AJC regulates epithelial morphogenesis and remodeling processes. The AJC consists of tight and adherens junctions, functions as a barrier and boundary, and plays a role in signal transduction. Endothelial junction proteins play important roles in tissue integrity and vascular permeability, leukocyte extravasation, and angiogenesis. Air pollutants such as particulate matter, ozone, and biologic contaminants penetrate deep into the airways, reaching the bronchioles and alveoli before entering the bloodstream to trigger airway inflammation. Pollutants accumulating in the lungs exacerbate the symptoms of respiratory diseases, including asthma and chronic obstructive lung disease. Biological contaminants include bacteria, viruses, animal dander and cat saliva, house dust mites, cockroaches, and pollen. Allergic inflammation develops in tissues such as the lung and skin with large epithelial surface areas exposed to the environment. Barrier dysfunction in the lung allows allergens and environmental pollutants to activate the epithelium and produce cytokines that promote the induction and development of immune responses. In this article, we review the impact of environmental pollutants on the cell barrier in respiratory diseases.
Keywords: Air pollution; asthma; barrier; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; environmental pollutants; epithelium; house dust mites; ozone; particulate matter.
Copyright © 2021 The Korean Academy of Asthma, Allergy and Clinical Immunology • The Korean Academy of Pediatric Allergy and Respiratory Disease.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no financial or other issues that might lead to conflict of interest.
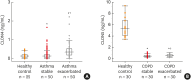
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of Air Pollutants on Airway Diseases.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Sep 20;18(18):9905. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18189905. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34574829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From triggers to asthma: a narrative review on epithelium dysfunction.Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022 Nov;54(6):247-257. doi: 10.23822/EurAnnACI.1764-1489.271. Epub 2022 Oct 10. Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36214074 Review.
-
Impact of particulate air pollution on airway injury and epithelial plasticity; underlying mechanisms.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 8;15:1324552. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1324552. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38524119 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of concentrated ambient particles on normal and hypersecretory airways in rats.Res Rep Health Eff Inst. 2004 Aug;(120):1-68; discussion 69-79. Res Rep Health Eff Inst. 2004. PMID: 15543855
-
Environmental factors in epithelial barrier dysfunction.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020 Jun;145(6):1517-1528. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.04.024. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32507229 Review.
Cited by
-
Korean Red Ginseng water extract inhibits cadmium-induced lung injury via suppressing MAPK/ERK1/2/AP-1 pathway.J Ginseng Res. 2022 Sep;46(5):690-699. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2022.04.003. Epub 2022 May 4. J Ginseng Res. 2022. PMID: 36090678 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering the Effects of 2D Black Phosphorus on Disrupted Hematopoiesis and Pulmonary Immune Homeostasis Using a Developed Flow Cytometry Method.Environ Sci Technol. 2022 Nov 15;56(22):15869-15881. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.2c03675. Epub 2022 Oct 13. Environ Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 36227752 Free PMC article.
-
Transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 channel inhibition attenuates lung ischemia-reperfusion injury in a porcine lung transplant model.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2024 Oct;168(4):e121-e132. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2024.03.001. Epub 2024 Apr 27. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2024. PMID: 38678474
-
Impact of the Junction Adhesion Molecule-A on Asthma.Yonsei Med J. 2023 Jun;64(6):375-383. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2022.0503. Yonsei Med J. 2023. PMID: 37226564 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidants prevent particulate matter-induced senescence of lung fibroblasts.Heliyon. 2023 Mar 1;9(3):e14179. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14179. eCollection 2023 Mar. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 36915477 Free PMC article.

