c-Abl kinase regulates neutrophil extracellular trap formation and lung injury in abdominal sepsis
- PMID: 34732849
- PMCID: PMC8860741
- DOI: 10.1038/s41374-021-00683-6
c-Abl kinase regulates neutrophil extracellular trap formation and lung injury in abdominal sepsis
Abstract
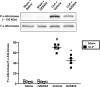
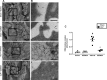
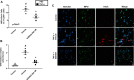
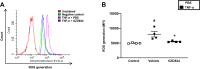
Sepsis is associated with exaggerated neutrophil responses although mechanisms remain elusive. The aim of this study was to investigate the role of c-Abelson (c-Abl) kinase in neutrophil extracellular trap (NET) formation and inflammation in septic lung injury. Abdominal sepsis was induced by cecal ligation and puncture (CLP). NETs were detected by electron microscopy in the lung and by confocal microscopy in vitro. Plasma levels of DNA-histone complexes, interleukin-6 (IL-6) and CXC chemokines were quantified. CLP-induced enhanced phosphorylation of c-Abl kinase in circulating neutrophils. Administration of the c-Abl kinase inhibitor GZD824 not only abolished activation of c-Abl kinase in neutrophils but also reduced NET formation in the lung and plasma levels of DNA-histone complexes in CLP mice. Moreover, inhibition of c-Abl kinase decreased CLP-induced lung edema and injury. Administration of GDZ824 reduced CLP-induced increases in the number of alveolar neutrophils. Inhibition of c-Abl kinase also markedly attenuated levels of CXC chemokines in the lung and plasma as well as IL-6 levels in the plasma of septic animals. Taken together, this study demonstrates that c-Abl kinase is a potent regulator of NET formation and we conclude that c-Abl kinase might be a useful target to ameliorate lung damage in abdominal sepsis.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
c-Abl kinase regulates neutrophil extracellular trap formation, inflammation, and tissue damage in severe acute pancreatitis.J Leukoc Biol. 2019 Aug;106(2):455-466. doi: 10.1002/JLB.3A0618-222RR. Epub 2019 Mar 12. J Leukoc Biol. 2019. PMID: 30861207
-
Rho-kinase signaling regulates pulmonary infiltration of neutrophils in abdominal sepsis via attenuation of CXC chemokine formation and Mac-1 expression on neutrophils.Shock. 2012 Mar;37(3):282-8. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e3182426be4. Shock. 2012. PMID: 22266975
-
MiR-155 regulates neutrophil extracellular trap formation and lung injury in abdominal sepsis.J Leukoc Biol. 2022 Feb;111(2):391-400. doi: 10.1002/JLB.3A1220-789RR. Epub 2021 Jun 11. J Leukoc Biol. 2022. PMID: 34114683
-
Senkyunolide I protect against lung injury via inhibiting formation of neutrophil extracellular trap in a murine model of cecal ligation and puncture.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Oct;99:107922. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107922. Epub 2021 Jul 2. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34224996
-
Proinflammatory role of neutrophil extracellular traps in abdominal sepsis.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014 Oct 1;307(7):L586-96. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00365.2013. Epub 2014 Aug 1. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25085626
Cited by
-
From pancreas to lungs: The role of immune cells in severe acute pancreatitis and acute lung injury.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024 Jul;12(7):e1351. doi: 10.1002/iid3.1351. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024. PMID: 39023414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neutrophil extracellular traps promote erectile dysfunction in rats with diabetes mellitus by enhancing NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 16;14(1):16457. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-67281-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39014129 Free PMC article.
-
Role of neutrophil extracellular traps in inflammatory evolution in severe acute pancreatitis.Chin Med J (Engl). 2022 Dec 5;135(23):2773-2784. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002359. Chin Med J (Engl). 2022. PMID: 36729096 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Levi M, van der Poll T. Inflammation and coagulation. Crit. Care Med. 2010;38:S26–S34. - PubMed
-
- Asaduzzaman M, Zhang S, Lavasani S, Wang Y, Thorlacius H. LFA-1 and MAC-1 mediate pulmonary recruitment of neutrophils and tissue damage in abdominal sepsis. Shock. 2008;30:254–259. - PubMed
-
- Nagase T, et al. Acute lung injury by sepsis and acid aspiration: a key role for cytosolic phospholipase A2. Nat. Immunol. 2000;1:42–46. - PubMed
-
- Parrillo JE. Pathogenetic mechanisms of septic shock. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993;328:1471–1477. - PubMed
-
- Kamochi M, et al. P-selectin and ICAM-1 mediate endotoxin-induced neutrophil recruitment and injury to the lung and liver. Am. J. Physiol. 1999;277:L310–L319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

