Virtual 2D mapping of the viral proteome reveals host-specific modality distribution of molecular weight and isoelectric point
- PMID: 34711905
- PMCID: PMC8553790
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-00797-3
Virtual 2D mapping of the viral proteome reveals host-specific modality distribution of molecular weight and isoelectric point
Abstract
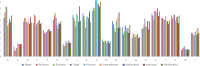
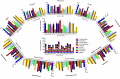
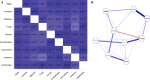
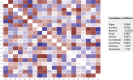
A proteome-wide study of the virus kingdom based on 1.713 million protein sequences from 19,128 virus proteomes was conducted to construct an overall proteome map of the virus kingdom. Viral proteomes encode an average of 386.214 amino acids per protein with the variation in the number of protein-coding sequences being host-specific. The proteomes of viruses of fungi hosts (882.464) encoded the greatest number of amino acids, while the viral proteome of bacterial host (210.912) encoded the smallest number of amino acids. Viral proteomes were found to have a host-specific amino acid composition. Leu (8.556%) was the most abundant and Trp (1.274%) the least abundant amino acid in the collective proteome of viruses. Viruses were found to exhibit a host-dependent molecular weight and isoelectric point of encoded proteins. The isoelectric point (pI) of viral proteins was found in the acidic range, having an average pI of 6.89. However, the pI of viral proteins of algal (pI 7.08) and vertebrate (pI 7.09) hosts was in the basic range. The virtual 2D map of the viral proteome from different hosts exhibited host-dependent modalities. The virus proteome from algal hosts and archaea exhibited a bimodal distribution of molecular weight and pI, while the virus proteome of bacterial host exhibited a trimodal distribution, and the virus proteome of fungal, human, land plants, invertebrate, protozoa, and vertebrate hosts exhibited a unimodal distribution.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Virtual 2-D map of the fungal proteome.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 23;11(1):6676. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86201-6. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33758316 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding the Virtual 2D Map of the Chloroplast Proteomes.Biol Proced Online. 2022 Dec 13;24(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s12575-022-00186-8. Biol Proced Online. 2022. PMID: 36513972 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular mass and isoelectric point of plant proteomes.BMC Genomics. 2019 Aug 5;20(1):631. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5983-8. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31382875 Free PMC article.
-
Viral proteomics: global evaluation of viruses and their interaction with the host.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2007 Dec;4(6):815-29. doi: 10.1586/14789450.4.6.815. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2007. PMID: 18067418 Review.
-
Viral proteomics.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2007 Jun;71(2):398-411. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00042-06. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2007. PMID: 17554050 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Virtual 2D map of cyanobacterial proteomes.PLoS One. 2022 Oct 3;17(10):e0275148. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0275148. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36190972 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gelderblom, H. Structure and classification of viruses. In Medical Microbiology, Chapter 41 (1996). - PubMed
-
- Wessner D. The origins of viruses. Nat. Educ. 2010;3:37.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

