Identification and characterization of a novel glutaminase inhibitor
- PMID: 34698439
- PMCID: PMC8727943
- DOI: 10.1002/2211-5463.13319
Identification and characterization of a novel glutaminase inhibitor
Abstract
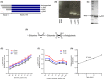
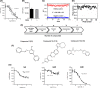
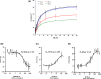
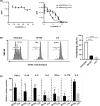
In humans, there are two forms of glutaminase (GLS), designated GLS1 and GLS2. These enzymes catalyse the conversion of glutamine to glutamate. GLS1 exists as two isozymes: kidney glutaminase (KGA) and glutaminase C (GAC). Several GLS inhibitors have been identified, of which DON (6-diazo-5-oxonorleucine), BPTES (bis-2-(5-phenylacetamido-1, 3, 4-thiadiazol-2-yl) ethyl sulphide), 968 (5-(3-Bromo-4-(dimethylamino)phenyl)-2,2-dimethyl-2,3,5,6-tetrahydrobenzo[a]phenanthridin-4(1H)-one) and CB839 (Telaglenastat) are the most widely used. However, these inhibitors have variable efficacy, specificity and bioavailability in research and clinical settings, implying the need for novel and improved GLS inhibitors. Based on this need, a diverse library of 28,000 compounds from Enamine was screened for inhibition of recombinant, purified GAC. From this library, one inhibitor designated compound 19 (C19) was identified with kinetic features revealing allosteric inhibition of GAC in the µm range. Moreover, C19 inhibits anti-CD3/CD28-induced CD4+ T-cell proliferation and cytokine production with similar or greater potency as compared to BPTES. Taken together, our data suggest that C19 has the potential to modulate GLS1 activity and alter metabolic activity of T cells.
Keywords: BPTES; CB839; CD4+ T cells; GAC; GLS inhibitor; high-throughput screening.
© 2021 The Authors. FEBS Open Bio published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of the interactions of potent allosteric inhibitors with glutaminase C, a key enzyme in cancer cell glutamine metabolism.J Biol Chem. 2018 Mar 9;293(10):3535-3545. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.810101. Epub 2018 Jan 9. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29317493 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibiting glutaminase in acute myeloid leukemia: metabolic dependency of selected AML subtypes.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 29;7(48):79722-79735. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12944. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27806325 Free PMC article.
-
Novel mechanism of inhibition of rat kidney-type glutaminase by bis-2-(5-phenylacetamido-1,2,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)ethyl sulfide (BPTES).Biochem J. 2007 Sep 15;406(3):407-14. doi: 10.1042/BJ20070039. Biochem J. 2007. PMID: 17581113 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Progress in the Discovery of Allosteric Inhibitors of Kidney-Type Glutaminase.J Med Chem. 2019 Jan 10;62(1):46-59. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b00327. Epub 2018 Jul 3. J Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 29969024 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Development of Small Molecule Glutaminase Inhibitors.Curr Top Med Chem. 2018;18(6):432-443. doi: 10.2174/1568026618666180525100830. Curr Top Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29793408 Review.
Cited by
-
Glutaminolysis and CD4+ T-cell metabolism in autoimmunity: From pathogenesis to therapy prospects.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 23;13:986847. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.986847. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36211442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolomics-driven approaches for identifying therapeutic targets in drug discovery.MedComm (2020). 2024 Nov 11;5(11):e792. doi: 10.1002/mco2.792. eCollection 2024 Nov. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39534557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glutaminolysis of CD4+ T Cells: A Potential Therapeutic Target in Viral Diseases.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Feb 1;17:603-616. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S443482. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38318243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glutaminolysis and peripheral CD4+ T cell differentiation: from mechanism to intervention strategy.Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 21;14:1221530. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1221530. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37545506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic Heterogeneity, Plasticity, and Adaptation to "Glutamine Addiction" in Cancer Cells: The Role of Glutaminase and the GTωA [Glutamine Transaminase-ω-Amidase (Glutaminase II)] Pathway.Biology (Basel). 2023 Aug 14;12(8):1131. doi: 10.3390/biology12081131. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627015 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Perera SY, Chen TC, Curthoys NP. Biosynthesis and processing of renal mitochondrial glutaminase in cultured proximal tubular epithelial‐cells and in isolated‐mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:17764–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

