Nanotechnology Interventions in the Management of COVID-19: Prevention, Diagnosis and Virus-Like Particle Vaccines
- PMID: 34696237
- PMCID: PMC8537718
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines9101129
Nanotechnology Interventions in the Management of COVID-19: Prevention, Diagnosis and Virus-Like Particle Vaccines
Abstract
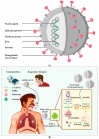
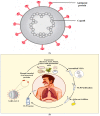
SARS-CoV-2 claimed numerous lives and put nations on high alert. The lack of antiviral medications and the small number of approved vaccines, as well as the recurrence of adverse effects, necessitates the development of novel treatment ways to combat COVID-19. In this context, using databases such as PubMed, Google Scholar, and Science Direct, we gathered information about nanotechnology's involvement in the prevention, diagnosis and virus-like particle vaccine development. This review revealed that various nanomaterials like gold, polymeric, graphene and poly amino ester with carboxyl group coated magnetic nanoparticles have been explored for the fast detection of SARS-CoV-2. Personal protective equipment fabricated with nanoparticles, such as gloves, masks, clothes, surfactants, and Ag, TiO2 based disinfectants played an essential role in halting COVID-19 transmission. Nanoparticles are used not only in vaccine delivery, such as lipid nanoparticles mediated transport of mRNA-based Pfizer and Moderna vaccines, but also in the development of vaccine as the virus-like particles elicit an immune response. There are now 18 virus-like particle vaccines in pre-clinical development, with one of them, developed by Novavax, reported being in phase 3 trials. Due to the probability of upcoming COVID-19 waves, and the rise of new diseases, the future relevance of virus-like particles is imperative. Furthermore, psychosocial variables linked to vaccine reluctance constitute a critical problem that must be addressed immediately to avert pandemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; diagnosis; prevention; virus-like particle vaccines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
COVID-19 vaccines: comparison of biological, pharmacological characteristics and adverse effects of Pfizer/BioNTech and Moderna Vaccines.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021 Feb;25(3):1663-1669. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202102_24877. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33629336 Review.
-
The Rapid Development and Early Success of Covid 19 Vaccines Have Raised Hopes for Accelerating the Cancer Treatment Mechanism.Arch Razi Inst. 2021 Mar;76(1):1-6. doi: 10.22092/ari.2021.353761.1612. Epub 2021 Mar 1. Arch Razi Inst. 2021. PMID: 33818952 Free PMC article.
-
Toward Nanotechnology-Enabled Approaches against the COVID-19 Pandemic.ACS Nano. 2020 Jun 23;14(6):6383-6406. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c03697. Epub 2020 Jun 10. ACS Nano. 2020. PMID: 32519842 Review.
-
The British variant of the new coronavirus-19 (Sars-Cov-2) should not create a vaccine problem.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2021 Jan-Feb;35(1):1-4. doi: 10.23812/21-3-E. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2021. PMID: 33377359
-
Review of COVID-19 Vaccines Approved in the United States of America for Emergency Use.J Clin Med Res. 2021 Apr;13(4):204-213. doi: 10.14740/jocmr4490. Epub 2021 Apr 27. J Clin Med Res. 2021. PMID: 34007358 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antibacterial and Antiviral Effects of Ag, Cu and Zn Metals, Respective Nanoparticles and Filter Materials Thereof against Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 and Influenza A Virus.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Nov 22;14(12):2549. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14122549. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36559043 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements of Nanotechnology and Nanomaterials in Environmental and Human Protection for Combatting the COVID-19 During and Post-pandemic Era: A Comprehensive Scientific Review.Biomed Mater Devices. 2023 May 10:1-24. doi: 10.1007/s44174-023-00086-9. Online ahead of print. Biomed Mater Devices. 2023. PMID: 37363141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integration of ZnO nanorods with silver ions by a facile co-precipitation for antimicrobial, larvicidal, and ovicidal activity.BMC Biotechnol. 2023 Jul 20;23(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s12896-023-00790-w. BMC Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37474922 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang J., Shen J., Ye D., Yan X., Zhang Y., Yang W., Li X., Wang J., Zhang L., Pan L. Disinfection technology of hospital wastes and wastewater: Suggestions for disinfection strategy during coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic in China. Environ. Pollut. 2020;262:114665. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114665. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

