Circulating MicroRNAs as Biomarkers of Accelerated Sarcopenia in Chronic Heart Failure
- PMID: 34692380
- PMCID: PMC8415175
- DOI: 10.5334/gh.943
Circulating MicroRNAs as Biomarkers of Accelerated Sarcopenia in Chronic Heart Failure
Abstract
Background: Sarcopenia is a critical finding in patients with chronic heart failure (CHF). However, the search for a definitive biomarker to predict muscle and functional decline in CHF remains elusive.
Objectives: We aimed to correlate the circulating levels of selected miRs with the indexes of sarcopenia during healthy aging and in patients with CHF.
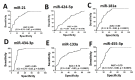
Methods: We analyzed the association of circulating microRNAs (miRs) levels including miR-21, miR-434-3p, miR424-5p, miR-133a, miR-455-3p and miR-181a with sarcopenia indexes in male, 61-73 years old healthy controls and patients with CHF (N = 89-92/group).
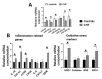
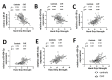
Results: Patients with CHF had lower hand-grip strength (HGS), appendicular skeletal mass index (ASMI) and physical capacity than healthy controls. Circulating miR-21 levels were higher and miR-181a, miR-133a, miR-434-3p and miR-455-3p levels were lower in patients with CHF than healthy controls. Among the sarcopenia indexes, HGS showed the strongest correlation with miR-133a while ASMI showed the strongest correlations with miR-133a, miR-434-3p and miR-455-3p. Among the miRs, miR-434-3p showed the highest area under the curve in testing for sensitivity and specificity for CHF. These changes were associated with higher expressions of the markers of inflammation, oxidative stress and muscle damage in CHF patients.
Conclusion: Taken together, our data show that circulating miRs can be useful markers of muscle health and physical capacity in the sarcopenic elderly with CHF.
Keywords: Sarcopenia; hand-grip strength; heart failure; microRNAs.
Copyright: © 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Circulating miRNA-1-3p as Biomarker of Accelerated Sarcopenia in Patients Diagnosed with Chronic Heart Failure.Rev Invest Clin. 2022;74(5):276-268. doi: 10.24875/RIC.22000151. Rev Invest Clin. 2022. PMID: 36328028
-
Circulating Biomarkers of Accelerated Sarcopenia in Respiratory Diseases.Biology (Basel). 2020 Oct 3;9(10):322. doi: 10.3390/biology9100322. Biology (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33023021 Free PMC article.
-
Bone and muscle specific circulating microRNAs in postmenopausal women based on osteoporosis and sarcopenia status.Bone. 2019 Mar;120:271-278. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2018.11.001. Epub 2018 Nov 5. Bone. 2019. PMID: 30408612
-
Osteoporosis, fracture, osteoarthritis & sarcopenia: A systematic review of circulating microRNA association.Bone. 2021 Nov;152:116068. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2021.116068. Epub 2021 Jun 22. Bone. 2021. PMID: 34166859 Review.
-
Candidate microRNAs as prognostic biomarkers in heart failure: A systematic review.Rev Port Cardiol. 2022 Oct;41(10):865-885. doi: 10.1016/j.repc.2021.03.020. Epub 2022 Aug 3. Rev Port Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 36207069 Review. English, Portuguese.
Cited by
-
The role of non-coding RNAs in muscle aging: regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic potential.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Jan 9;10:1308274. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1308274. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38264571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A leaky gut contributes to reduced sarcopenia-related quality of life (SarQoL) in geriatric older adults.Qual Life Res. 2024 Feb;33(2):551-559. doi: 10.1007/s11136-023-03547-2. Epub 2023 Nov 6. Qual Life Res. 2024. PMID: 37930557
-
Sarcopenia and Frailty in Heart Failure: Is There a Biomarker Signature?Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2022 Dec;19(6):400-411. doi: 10.1007/s11897-022-00575-w. Epub 2022 Oct 20. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2022. PMID: 36261756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of circulating hsa-miRNAs with sarcopenia: the SarcoPhAge study.Aging Clin Exp Res. 2024 Mar 14;36(1):70. doi: 10.1007/s40520-024-02711-z. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2024. PMID: 38485856 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating miR-29b decrease in response to sarcopenia in patients with cardiovascular risk factors in older Chinese.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Dec 20;9:1094388. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.1094388. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36606278 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

