Impact of Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Cancer Metabolism and Immune Status
- PMID: 34687175
- PMCID: PMC8948647
- DOI: 10.1002/hep4.1838
Impact of Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Cancer Metabolism and Immune Status
Abstract
We examined phosphorylated nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (P-NRF2) expression in surgically resected primary hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and investigated the association of P-NRF2 expression with clinicopathological features and patient outcome. We also evaluated the relationship among NRF2, cancer metabolism, and programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression. In this retrospective study, immunohistochemical staining of P-NRF2 was performed on the samples of 335 patients who underwent hepatic resection for HCC. Tomography/computed tomography using fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose was performed, and HCC cell lines after NRF2 knockdown were analyzed by array. We also analyzed the expression of PD-L1 after hypoxia inducible factor 1α (HIF1A) knockdown in NRF2-overexpressing HCC cell lines. Samples from 121 patients (36.1%) were positive for P-NRF2. Positive P-NRF2 expression was significantly associated with high alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) expression, a high rate of poor differentiation, and microscopic intrahepatic metastasis. In addition, positive P-NRF2 expression was an independent predictor for recurrence-free survival and overall survival. NRF2 regulated glucose transporter 1, hexokinase 2, pyruvate kinase isoenzymes L/R, and phosphoglycerate kinase 1 expression and was related to the maximum standardized uptake value. PD-L1 protein expression levels were increased through hypoxia-inducible factor 1α after NRF2 overexpression in HCC cells. Conclusions: Our large cohort study revealed that P-NRF2 expression in cancer cells was associated with clinical outcome in HCC. Additionally, we found that NRF2 was located upstream of cancer metabolism and tumor immunity.
© 2021 The Authors. Hepatology Communications published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Figures
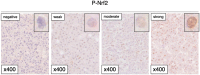
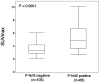
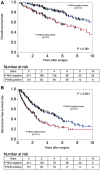
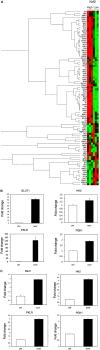
Similar articles
-
ARID1A Deficiency Is Associated With High Programmed Death Ligand 1 Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Hepatol Commun. 2020 Dec 30;5(4):675-688. doi: 10.1002/hep4.1659. eCollection 2021 Apr. Hepatol Commun. 2020. PMID: 33860125 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Nqo1 activity intercepts anoikis resistance and reduces metastatic potential of hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Sci. 2020 Apr;111(4):1228-1240. doi: 10.1111/cas.14320. Epub 2020 Mar 3. Cancer Sci. 2020. PMID: 31968140 Free PMC article.
-
CMTM6 Stabilizes PD-L1 Expression and Is a New Prognostic Impact Factor in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Hepatol Commun. 2020 Nov 24;5(2):334-348. doi: 10.1002/hep4.1643. eCollection 2021 Feb. Hepatol Commun. 2020. PMID: 33553979 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Hepatocellular Carcinoma Induction by Aberrant NRF2 Activation-Mediated Transcription Networks: Interaction of NRF2-KEAP1 Controls the Fate of Hepatocarcinogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 29;21(15):5378. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155378. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32751080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1)/programmed death-ligand-1 (PD-L1) axis in hepatocellular carcinoma: prognostic and therapeutic perspectives.Clin Transl Oncol. 2019 Jun;21(6):702-712. doi: 10.1007/s12094-018-1975-4. Epub 2018 Nov 1. Clin Transl Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30387047 Review.
Cited by
-
Determinants of the maximal functional reserve during repeated supramaximal exercise by humans: The roles of Nrf2/Keap1, antioxidant proteins, muscle phenotype and oxygenation.Redox Biol. 2023 Oct;66:102859. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102859. Epub 2023 Aug 22. Redox Biol. 2023. PMID: 37666117 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidants-related nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 gene variants associated with HBV-related liver disease.Cancer Cell Int. 2023 Apr 16;23(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s12935-023-02918-6. Cancer Cell Int. 2023. PMID: 37062839 Free PMC article.
-
Breaking the Barriers of Therapy Resistance: Harnessing Ferroptosis for Effective Hepatocellular Carcinoma Therapy.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024 Jul 2;11:1265-1278. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S469449. eCollection 2024. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024. PMID: 38974015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Significance of Signal Regulatory Protein Alpha (SIRPα) Expression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Ann Surg Oncol. 2023 Jun;30(6):3378-3389. doi: 10.1245/s10434-022-13058-y. Epub 2023 Jan 15. Ann Surg Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36641515
-
Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote tumor cell growth via miR-493-5p in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.Cancer Sci. 2023 Mar;114(3):937-947. doi: 10.1111/cas.15644. Epub 2022 Dec 8. Cancer Sci. 2023. PMID: 36369960 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Villanueva A. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 2019;380:1450‐1462. - PubMed
-
- Itoh S, Morita K, Ueda S, Sugimachi K, Yamashita Y‐I, Gion T, et al. Long‐term results of hepatic resection combined with intraoperative local ablation therapy for patients with multinodular hepatocellular carcinomas. Ann Surg Oncol 2009;16:3299‐3307. - PubMed
-
- Itoh S, Shirabe K, Taketomi A, Morita K, Harimoto N, Tsujita E, et al. Zero mortality in more than 300 hepatic resections: validity of preoperative volumetric analysis. Surg Today 2012;42:435‐440. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

