Functional Depletion of HSP72 by siRNA and Quercetin Enhances Vorinostat-Induced Apoptosis in an HSP72-Overexpressing Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma Cell Line, Hut78
- PMID: 34681913
- PMCID: PMC8541672
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms222011258
Functional Depletion of HSP72 by siRNA and Quercetin Enhances Vorinostat-Induced Apoptosis in an HSP72-Overexpressing Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma Cell Line, Hut78
Abstract
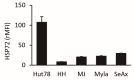
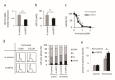
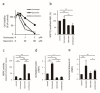
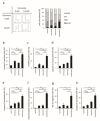
Histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACis) are one of the therapeutic options for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL), but they have limited effects. We previously demonstrated that HSP72 overexpression is associated with chemoresistance to HDACis in lymphoma cells. The purpose of this study was to investigate whether the functional depletion of HSP72 enhances the effect of the HDACi vorinostat. First, we established a stable HSP72-knockdown CTCL cell line and confirmed the influence of HSP72 reduction on the antitumor effects of vorinostat. Next, we studied the effect of quercetin, an inhibitor of HSP72, on the antineoplastic effects of vorinostat. In five CTCL cell lines examined, HSP72 expression was highest in Hut78 cells, and HSP72 knockdown enhanced vorinostat-induced apoptosis in these cells. Low-dose quercetin reduced HSP72 expression, increased HDAC activity, and enhanced vorinostat-induced suppression of Hut78 cell proliferation. A single low dose of quercetin induced G2 arrest and only slightly increased the sub-G1 cell fraction. Quercetin also significantly enhanced vorinostat-induced apoptosis, caspase-3, caspase-8, and caspase-9 activity, and the loss of mitochondrial membrane potential. HSP72 knockdown enhanced vorinostat-induced apoptosis in an HSP72-overexpressing CTCL cell line, and thus, quercetin may be a suitable candidate for combination therapy with vorinostat in clinical settings.
Keywords: HSP72; combination therapy; cutaneous T-cell lymphoma; histone deacetylase inhibitor; quercetin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Kinome profiling analysis identified Src pathway as a novel therapeutic target in combination with histone deacetylase inhibitors for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.J Dermatol Sci. 2021 Mar;101(3):194-201. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2021.01.004. Epub 2021 Jan 22. J Dermatol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33531202
-
HSP72 functionally inhibits the anti-neoplastic effects of HDAC inhibitors.J Dermatol Sci. 2018 Apr;90(1):82-89. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2018.01.002. Epub 2018 Jan 31. J Dermatol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29395577
-
Histone deacetylase inhibitors inhibit metastasis by restoring a tumor suppressive microRNA-150 in advanced cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 31;8(5):7572-7585. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13810. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27935859 Free PMC article.
-
Vorinostat: A novel therapy for the treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2010 May 15;67(10):793-7. doi: 10.2146/ajhp090247. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2010. PMID: 20479100 Review.
-
HDAC inhibitors for the treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphomas.Future Med Chem. 2012 Mar;4(4):471-86. doi: 10.4155/fmc.12.6. Future Med Chem. 2012. PMID: 22416775 Review.
Cited by
-
Heat shock proteins as hallmarks of cancer: insights from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic strategies.J Hematol Oncol. 2024 Sep 4;17(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s13045-024-01601-1. J Hematol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39232809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetics: Mechanisms, potential roles, and therapeutic strategies in cancer progression.Genes Dis. 2023 Jul 6;11(5):101020. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2023.04.040. eCollection 2024 Sep. Genes Dis. 2023. PMID: 38988323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Flavonoids Regulate Redox-Responsive Transcription Factors in Glioblastoma and Microglia.Cells. 2023 Dec 12;12(24):2821. doi: 10.3390/cells12242821. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38132142 Free PMC article.
-
DIGE-Based Biomarker Discovery in Blood Cancers.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2596:105-112. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2831-7_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36378434
-
Is It Still Possible to Think about HSP70 as a Therapeutic Target in Onco-Hematological Diseases?Biomolecules. 2023 Mar 28;13(4):604. doi: 10.3390/biom13040604. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37189352 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Swerdlow S.H., Campo E., Pileri S.A., Harris N.L., Stein H., Siebert R., Advani R., Ghielmini M., Salles G.A., Zelenetz A.D., et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood. 2016;127:2375–2390. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-01-643569. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hughes C.F., Khot A., McCormack C., Lade S., Westerman D.A., Twigger R., Buelens O., Newland K., Tam C., Dickinson M., et al. Lack of durable disease control with chemotherapy for mycosis fungoides and Sezary syndrome: A comparative study of systemic therapy. Blood. 2015;125:71–81. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-07-588236. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

