Research Progress in Chinese Herbal Medicines for Treatment of Sepsis: Pharmacological Action, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacokinetics
- PMID: 34681737
- PMCID: PMC8540716
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms222011078
Research Progress in Chinese Herbal Medicines for Treatment of Sepsis: Pharmacological Action, Phytochemistry, and Pharmacokinetics
Abstract
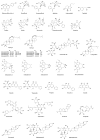
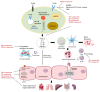
Sepsis is a life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection; the pathophysiology of sepsis is complex. The incidence of sepsis is steadily increasing, with worldwide mortality ranging between 30% and 50%. Current treatment approaches mainly rely on the timely and appropriate administration of antimicrobials and supportive therapies, but the search for pharmacotherapies modulating the host response has been unsuccessful. Chinese herbal medicines, i.e., Chinese patent medicines, Chinese herbal prescriptions, and single Chinese herbs, play an important role in the treatment of sepsis through multicomponent, multipathway, and multitargeting abilities and have been officially recommended for the management of COVID-19. Chinese herbal medicines have therapeutic actions promising for the treatment of sepsis; basic scientific research on these medicines is increasing. However, the material bases of most Chinese herbal medicines and their underlying mechanisms of action have not yet been fully elucidated. This review summarizes the current studies of Chinese herbal medicines used for the treatment of sepsis in terms of clinical efficacy and safety, pharmacological activity, phytochemistry, bioactive constituents, mechanisms of action, and pharmacokinetics, to provide an important foundation for clarifying the pathogenesis of sepsis and developing novel antisepsis drugs based on Chinese herbal medicines.
Keywords: Chinese herbal medicines; Qingwen Baidu decoction; Shengfu injection; Shengmai; Xuanbai Chengqi decoction; XueBiJing injection; antiseptic actions; material basis; sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Analysis of medication characteristics of traditional Chinese medicine in treating COVID-19 based on data mining].Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2020 May 25;49(2):260-269. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9292.2020.03.14. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2020. PMID: 32391675 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Chinese herbal medicine: Fighting SARS-CoV-2 infection on all fronts.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Apr 24;270:113869. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.113869. Epub 2021 Jan 21. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33485973 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional Chinese Medicine as the Preventive and Therapeutic Remedy for COVID-19.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(21):3118-3131. doi: 10.2174/0929867330666230331084126. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 36999715 Review.
-
Application of Chinese Medicine in the Management of Critical Conditions: A Review on Sepsis.Am J Chin Med. 2020;48(6):1315-1330. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X20500640. Epub 2020 Sep 9. Am J Chin Med. 2020. PMID: 32907362 Review.
-
Herbal medicines for viral myocarditis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Aug 28;(8):CD003711. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003711.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 03;(5):CD003711. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003711.pub6 PMID: 23986406 Updated. Review.
Cited by
-
Alterations in the gut microbiome and metabolome profiles of septic mice treated with Shen FuHuang formula.Front Microbiol. 2023 Mar 8;14:1111962. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1111962. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36970673 Free PMC article.
-
Berberine in Sepsis: Effects, Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Strategies.J Immunol Res. 2023 Jan 25;2023:4452414. doi: 10.1155/2023/4452414. eCollection 2023. J Immunol Res. 2023. PMID: 36741234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pseudorabies Virus: From Pathogenesis to Prevention Strategies.Viruses. 2022 Jul 27;14(8):1638. doi: 10.3390/v14081638. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36016260 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Nutraceutical Product Based on a Mixture of Algae and Extra Virgin Olive Oils and Olive Leaf Extract Attenuates Sepsis-Induced Cardiovascular and Muscle Alterations in Rats.Front Nutr. 2022 Jun 20;9:918841. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.918841. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35795581 Free PMC article.
-
Mitophagy and Ferroptosis in Sepsis-Induced ALI/ARDS: Molecular Mechanisms, Interactions and Therapeutic Prospects of Medicinal Plants.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Oct 29;17:7819-7835. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S488655. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39494205 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Singer M., Deutschman C.S., Seymour C.C., Shankar-Hari M., Annane D., Bauer M., Bellomo R., Bernard G.R., Chiche J.-D., Coopersmith C.C.M., et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3) JAMA. 2016;315:801–810. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fleischmann M.C., Scherag A., Adhikari N.K.J., Hartog C.S., Tsaganos T., Schlattmann P., Angus D.C., Reinhart K., on behalf of the International Forum Acute Care Trialists Assessment of Global Incidence and Mortality of Hospital-treated Sepsis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016;193:259–272. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201504-0781OC. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

