d-Amino Acids and pLG72 in Alzheimer's Disease and Schizophrenia
- PMID: 34681579
- PMCID: PMC8535920
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms222010917
d-Amino Acids and pLG72 in Alzheimer's Disease and Schizophrenia
Abstract
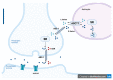
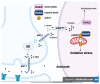
Numerous studies over the last several years have shown that d-amino acids, especially d-serine, have been related to brain and neurological disorders. Acknowledged neurological functions of d-amino acids include neurotransmission and learning and memory functions through modulating N-methyl-d-aspartate type glutamate receptors (NMDARs). Aberrant d-amino acids level and polymorphisms of genes related to d-amino acids metabolism are associated with neurodegenerative brain conditions. This review summarizes the roles of d-amino acids and pLG72, also known as d-amino acid oxidase activator, on two neurodegenerative disorders, schizophrenia and Alzheimer's disease (AD). The scope includes the changes in d-amino acids levels, gene polymorphisms of G72 genomics, and the role of pLG72 on NMDARs and mitochondria in schizophrenia and AD. The clinical diagnostic value of d-amino acids and pLG72 and the therapeutic importance are also reviewed.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; d-amino acids; pLG72; schizophrenia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biochemical Properties and Physiological Functions of pLG72: Twenty Years of Investigations.Biomolecules. 2022 Jun 20;12(6):858. doi: 10.3390/biom12060858. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35740983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
pLG72 levels increase in early phase of Alzheimer's disease but decrease in late phase.Sci Rep. 2019 Sep 13;9(1):13221. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-49522-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31520071 Free PMC article.
-
Regulating levels of the neuromodulator d-serine in human brain: structural insight into pLG72 and d-amino acid oxidase interaction.FEBS J. 2016 Sep;283(18):3353-70. doi: 10.1111/febs.13809. Epub 2016 Aug 5. FEBS J. 2016. PMID: 27400736
-
Advances in D-Amino Acids in Neurological Research.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 3;21(19):7325. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197325. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33023061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
D-Amino Acid Oxidase-pLG72 Interaction and D-Serine Modulation.Front Mol Biosci. 2018 Jan 24;5:3. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2018.00003. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Biosci. 2018. PMID: 29417050 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Polymer Conjugates of Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs) with d-Amino Acids (d-aa): State of the Art and Future Opportunities.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Feb 19;14(2):446. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14020446. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35214178 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolomics Study Suggests the Mechanism of Different Types of Tieguanyin (Oolong) Tea in Alleviating Alzheimer's Disease in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice.Metabolites. 2022 May 22;12(5):466. doi: 10.3390/metabo12050466. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 35629970 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of D-amino acid in Japanese post-fermented tea, Ishizuchi-kurocha.Biosci Microbiota Food Health. 2023;42(4):254-263. doi: 10.12938/bmfh.2023-005. Epub 2023 Jun 28. Biosci Microbiota Food Health. 2023. PMID: 37791341 Free PMC article.
-
Untargeted metabolomics analysis of the hippocampus and cerebral cortex identified the neuroprotective mechanisms of Bushen Tiansui formula in an aβ25-35-induced rat model of Alzheimer's disease.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 20;13:990307. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.990307. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36339577 Free PMC article.
-
Promising Application of D-Amino Acids toward Clinical Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 16;23(18):10794. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810794. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142706 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- NHRI-EX109-10731NI/National Health Research Institutes
- NHRI-EX110- 10816NC/National Health Research Institutes
- MOST 108-2410-H-039-009-MY2/Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan
- 109-2628-B-182A-002/Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan
- 109-2314-B-039-039-MY3/Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan
- 109-2314-B-039 -001/Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan
- 110-2314-B-182A-048/Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan
- 110-2622-B039-001/Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan
- CMRPG8G1391/Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Linkou
- CMRPG8K1162/Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Linkou
- CMRPG8K1461/Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Linkou
- CMU107-S-25/China Medical University, Taiwan
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

