The role of hypoxia-induced long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in tumorigenesis and metastasis
- PMID: 34654684
- PMCID: PMC8640553
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bj.2021.03.005
The role of hypoxia-induced long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in tumorigenesis and metastasis
Abstract
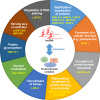
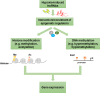
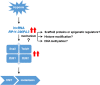
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are noncoding RNAs with length greater than 200 nt. The biological roles and mechanisms mediated by lncRNAs have been extensively investigated. Hypoxia is a proven microenvironmental factor that promotes solid tumor metastasis. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is one of the major mechanisms induced by hypoxia to contribute to metastasis. Many lncRNAs have been shown to be induced by hypoxia and their roles have been delineated. In this review, we focus on the hypoxia-inducible lncRNAs that interact with protein/protein complex and chromatin/epigenetic factors, and the mechanisms that contribute to metastasis. The role of a recently discovered lncRNA RP11-390F4.3 in hypoxia-induced EMT is discussed. Whole genome approaches to delineating the association between lncRNAs and histone modifications are discussed. Other topics related to hypoxia-induced tumor progression but require further investigation are also mentioned. The clinical significance and treatment strategy targeted against lncRNAs are discussed. The review aims to identify suitable lncRNA targets that may provide feasible therapeutic venues for hypoxia-involved cancers.
Keywords: Epigenetics; Epithelial–mesenchymal transition; Hypoxia; LncRNA RP11-390F4.3; Metastasis; lncRNAs.
Copyright © 2021 Chang Gung University. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest There is no competing interest among the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hypoxia-induced lncRNA RP11-390F4.3 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and metastasis through upregulating EMT regulators.Cancer Lett. 2020 Jul 28;483:35-45. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.04.014. Epub 2020 Apr 27. Cancer Lett. 2020. PMID: 32353468
-
Long non-coding RNA HOTTIP promotes hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of malignant glioma by regulating the miR-101/ZEB1 axis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Nov;95:711-720. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.08.133. Epub 2017 Sep 5. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28886531
-
Induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by hypoxia-induced lncRNA RP11-367G18.1 through regulating the histone 4 lysine 16 acetylation (H4K16Ac) mark.Am J Cancer Res. 2021 Jun 15;11(6):2618-2636. eCollection 2021. Am J Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34249418 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular regulation of hypoxia through the lenses of noncoding RNAs and epitranscriptome.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2023 Mar;14(2):e1750. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1750. Epub 2022 Jul 3. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2023. PMID: 35785444 Review.
-
Long noncoding RNAs: emerging regulators of tumor angiogenesis.Future Oncol. 2017 Jul;13(17):1551-1562. doi: 10.2217/fon-2017-0149. Epub 2017 May 17. Future Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28513194 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of a novel hypoxia-immune-related LncRNA risk signature for predicting the prognosis and immunotherapy response of colorectal cancer.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 14;13:951455. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.951455. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36189298 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor hypoxia: From basic knowledge to therapeutic implications.Semin Cancer Biol. 2023 Jan;88:172-186. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2022.12.011. Epub 2023 Jan 2. Semin Cancer Biol. 2023. PMID: 36603793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia-induced epigenetic regulation of breast cancer progression and the tumour microenvironment.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Aug 30;12:1421629. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1421629. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 39282472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia-driven ncRNAs in breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Jul 31;13:1207253. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1207253. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37583933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Greek gods and the double-edged sword of liver regeneration.Biomed J. 2021 Oct;44(5):515-520. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2021.10.010. Epub 2021 Oct 26. Biomed J. 2021. PMID: 34715410 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huarte M. The emerging role of lncRNAs in cancer. Nat Med. 2015;21:1253–1261. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

