Loss of TRIM31 promotes breast cancer progression through regulating K48- and K63-linked ubiquitination of p53
- PMID: 34650049
- PMCID: PMC8516922
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-021-04208-3
Loss of TRIM31 promotes breast cancer progression through regulating K48- and K63-linked ubiquitination of p53
Abstract
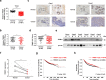
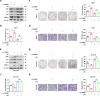
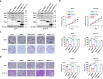
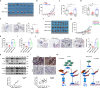
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in the world. Relapse and metastasis are important factors endangering the life of breast cancer patients, but the mechanism is still unclear. The stabilization of p53 is essential for preventing carcinogenesis, and ubiquitination is one of the main ways to regulate the stability of p53. Tripartite motif-containing 31 (TRIM31) is a new member of the TRIM family and functions as an E3 ubiquitin ligase. It acts as a cancer promoter or suppressor in the malignant processes of multiple cancers. However, the function of TRIM31 in breast cancer progression remains unknown. In this study, we showed that TRIM31 is downregulated in breast cancer tissues and negatively correlated with breast cancer progression. Both gain- and loss-of-function assays indicated that TRIM31 inhibits the proliferation, colony formation, migration, and invasion of breast cancer cells. Further investigation demonstrated that TRIM31 directly interacts with p53, and inducing the K63-linked ubiquitination of p53 via its RING domain, Meanwhile, TRIM31 suppresses the MDM2-mediated K48-linked ubiquitination of p53 through competitive inhibiting the interaction of MDM2 and p53, leading to the p53 stabilization and activation. Knockdown of p53 reversed the inhibitory effects of TRIM31 on the growth and metastasis of breast cancer cells. Moreover, we found that the RING and coiled-coil (C-C) domains of TRIM31 were essential for its tumor suppressor function. Taken together, our findings reveal a novel mechanism by which TRIM31 suppresses breast cancer development through the stabilization and activation of p53 and define a promising therapeutic strategy for restoring TRIM31 to treat breast cancer.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
TRIM31 is upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes disease progression by inducing ubiquitination of TSC1-TSC2 complex.Oncogene. 2018 Jan 25;37(4):478-488. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.349. Epub 2017 Oct 2. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 28967907
-
Knockdown of TRIM31 suppresses proliferation and invasion of gallbladder cancer cells by down-regulating MMP2/9 through the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Jul;103:1272-1278. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.04.120. Epub 2018 May 7. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29864908
-
TRIM45 functions as a tumor suppressor in the brain via its E3 ligase activity by stabilizing p53 through K63-linked ubiquitination.Cell Death Dis. 2017 May 25;8(5):e2831. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.149. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 28542145 Free PMC article.
-
E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM31: A potential therapeutic target.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Jul;176:116846. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116846. Epub 2024 Jun 7. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38850648 Review.
-
Emerging roles of tripartite motif family proteins (TRIMs) in breast cancer.Cancer Med. 2024 Jul;13(14):e7472. doi: 10.1002/cam4.7472. Cancer Med. 2024. PMID: 39016065 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Intricate confrontation: Research progress and application potential of TRIM family proteins in tumor immune escape.J Adv Res. 2023 Dec;54:147-179. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2023.01.011. Epub 2023 Feb 2. J Adv Res. 2023. PMID: 36736694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The E3 ubiquitin ligase TRIM31 attenuates NLRP3 inflammasome activation in Helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis by regulating ROS and autophagy.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Jan 3;21(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-00954-9. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 36597090 Free PMC article.
-
PLK3 promotes the proneural-mesenchymal transition in glioblastoma via transcriptional regulation of C5AR1.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Oct;50(10):8249-8258. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08716-7. Epub 2023 Aug 12. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37568042
-
Visualization of breast cancer-related protein synthesis from the perspective of bibliometric analysis.Eur J Med Res. 2023 Oct 27;28(1):461. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01364-4. Eur J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37885035 Free PMC article.
-
MDM2: current research status and prospects of tumor treatment.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 May 13;24(1):170. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03356-8. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 38741108 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 82072933/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81874071/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82072933/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81874071/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81773756/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82072933/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81874071/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81773756/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81874071/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81773756/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81874071/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81773756/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82072933/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81874071/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81773756/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81874071/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81773756/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81874071/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81773756/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82072933/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81874071/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81773756/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81874071/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 81773756/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82072933/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 2017SZ0060/Department of Science and Technology of Sichuan Province (Sichuan Provincial Department of Science and Technology)
- 2017SZ0060/Department of Science and Technology of Sichuan Province (Sichuan Provincial Department of Science and Technology)
- 2017SZ0060/Department of Science and Technology of Sichuan Province (Sichuan Provincial Department of Science and Technology)
- 2017SZ0060/Department of Science and Technology of Sichuan Province (Sichuan Provincial Department of Science and Technology)
- 2017SZ0060/Department of Science and Technology of Sichuan Province (Sichuan Provincial Department of Science and Technology)
- 2017SZ0060/Department of Science and Technology of Sichuan Province (Sichuan Provincial Department of Science and Technology)
- 2017SZ0060/Department of Science and Technology of Sichuan Province (Sichuan Provincial Department of Science and Technology)
- 2017SZ0060/Department of Science and Technology of Sichuan Province (Sichuan Provincial Department of Science and Technology)
- 2017SZ0060/Department of Science and Technology of Sichuan Province (Sichuan Provincial Department of Science and Technology)
- 2017SZ0060/Department of Science and Technology of Sichuan Province (Sichuan Provincial Department of Science and Technology)
- 2017SZ0060/Department of Science and Technology of Sichuan Province (Sichuan Provincial Department of Science and Technology)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

