Intramyocardial injection of human adipose-derived stem cells ameliorates cognitive deficit by regulating oxidative stress-mediated hippocampal damage after myocardial infarction
- PMID: 34633469
- PMCID: PMC8599314
- DOI: 10.1007/s00109-021-02135-6
Intramyocardial injection of human adipose-derived stem cells ameliorates cognitive deficit by regulating oxidative stress-mediated hippocampal damage after myocardial infarction
Abstract
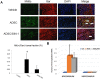
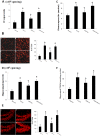
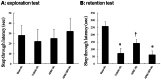
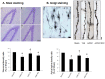
Cognitive impairment is a serious side effect of post-myocardial infarction (MI) course. We have recently demonstrated that human adipose-derived stem cells (hADSCs) ameliorated myocardial injury after MI by attenuating reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels. Here, we studied whether the beneficial effects of intramyocardial hADSC transplantation can extend to the brain and how they may attenuate cognitive dysfunction via modulating ROS after MI. After coronary ligation, male Wistar rats were randomized via an intramyocardial route to receive either vehicle, hADSC transplantation (1 × 106 cells), or the combination of hADSCs and 3-Morpholinosydnonimine (SIN-1, a peroxynitrite donor). Whether hADSCs migrated into the hippocampus was assessed by using human-specific primers in qPCR reactions. Passive avoidance test was used to assess cognitive performance. Postinfarction was associated with increased oxidative stress in the myocardium, circulation, and hippocampus. This was coupled with decreased numbers of dendritic spines as well as a significant downregulation of synaptic plasticity consisting of synaptophysin and PSD95. Step-through latency during passive avoidance test was impaired in vehicle-treated rats after MI. Intramyocardial hADSC injection exerted therapeutic benefits in improving cardiac function and cognitive impairment. None of hADSCs was detected in rat's hippocampus at the 3rd day after intramyocardial injection. The beneficial effects of hADSCs on MI-induced histological and cognitive changes were abolished after adding SIN-1. MI-induced ROS attacked the hippocampus to induce neurodegeneration, resulting in cognitive deficit. The remotely intramyocardial administration of hADSCs has the capacity of improved synaptic neuroplasticity in the hippocampus mediated by ROS, not the cell engraftment, after MI. KEY MESSAGES: Human adipose-derived stem cells (hADSCs) ameliorated injury after myocardial infarction by attenuating reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels. Intramyocardial administration of hADSCs remotely exerted therapeutic benefits in improving cognitive impairment after myocardial infarction. The improved synaptic neuroplasticity in the hippocampus was mediated by hADSC-inhibiting ROS, not by the stem cell engraftment.
Keywords: Cognitive function; Hippocampus; Human adipose-derived stem cells; Myocardial infarction; Passive avoidance test; Reactive oxygen species.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Host pre-conditioning improves human adipose-derived stem cell transplantation in ageing rats after myocardial infarction: Role of NLRP3 inflammasome.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Nov;24(21):12272-12284. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15403. Epub 2020 Oct 6. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 33022900 Free PMC article.
-
Remote transplantation of human adipose-derived stem cells induces regression of cardiac hypertrophy by regulating the macrophage polarization in spontaneously hypertensive rats.Redox Biol. 2019 Oct;27:101170. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101170. Epub 2019 Mar 21. Redox Biol. 2019. PMID: 31164286 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of neuron-derived neurotrophic factor on rejuvenation of human adipose-derived stem cells for cardiac repair after myocardial infarction.J Cell Mol Med. 2019 Sep;23(9):5981-5993. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.14456. Epub 2019 Jul 9. J Cell Mol Med. 2019. PMID: 31287219 Free PMC article.
-
Exendin-4 pretreated adipose derived stem cells are resistant to oxidative stress and improve cardiac performance via enhanced adhesion in the infarcted heart.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 10;9(6):e99756. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099756. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24915574 Free PMC article.
-
Rat adipose tissue-derived stem cells transplantation attenuates cardiac dysfunction post infarction and biopolymers enhance cell retention.PLoS One. 2010 Aug 10;5(8):e12077. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012077. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20711471 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Combination Therapy with Platelet-Rich Plasma and Epidermal Neural Crest Stem Cells Increases Treatment Efficacy in Vascular Dementia.Stem Cells Int. 2023 Dec 18;2023:3784843. doi: 10.1155/2023/3784843. eCollection 2023. Stem Cells Int. 2023. PMID: 38146481 Free PMC article.
-
Association between life's essential 8 and cognitive impairment in older patients: results from NHANES 2011-2014.BMC Geriatr. 2024 Nov 14;24(1):943. doi: 10.1186/s12877-024-05547-4. BMC Geriatr. 2024. PMID: 39543520 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dodson JA, Arnold SV, Reid KJ, Gill TM, Rich MW, Masoudi FA, Spertus JA, Krumholz HM, Alexander KP. Physical function and independence 1 year after myocardial infarction: observations from the Translational Research Investigating Underlying disparities in recovery from acute Myocardial infarction: Patients’ Health status registry. Am Heart J. 2012;163:790–796. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2012.02.024. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

