Compliant Underwater Manipulator with Integrated Tactile Sensor for Nonlinear Force Feedback Control of an SMA Actuation System
- PMID: 34629752
- PMCID: PMC8494145
- DOI: 10.1016/j.sna.2020.112221
Compliant Underwater Manipulator with Integrated Tactile Sensor for Nonlinear Force Feedback Control of an SMA Actuation System
Abstract
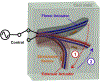
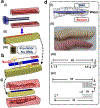
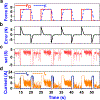
Design, sensing, and control of underwater gripping systems remain challenges for soft robotic manipulators. Our study investigates these critical issues by designing a shape memory alloy (SMA) actuation system for a soft robotic finger with a directly 3D-printed stretchable skin-like tactile sensor. SMA actuators were thermomechanically trained to assume a curved finger-like shape when Joule heated, and the flexible multi-layered tactile sensor was directly 3D-printed onto the surface of the fingertip. A nonlinear controller was developed to enable precise fingertip force control using feedback from the compliant tactile sensor. Underwater experiments were conducted using closed-loop force feedback from the directly 3D-printed tactile sensor with the SMA actuators, showing satisfactory force tracking ability. Furthermore, a 3D finite element model was developed to more deeply understand the shape memory thermal-fluidic-structural multi-physics simulation of the manipulator underwater. An application for human control via electromyogram (EMG) signals also demonstrated an intuitive way for a person to operate the submerged robotic finger. Together, these results suggested that the soft robotic finger could be used to carefully manipulate fragile objects underwater.
Keywords: Soft robot; electromyogram; multi-physics simulation; shape memory alloy; tactile sensor.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest 1. This manuscript is the authors’ original work and has not been published nor has it been submitted simultaneously elsewhere. 2. That all authors have checked the manuscript and have agreed to the submission.
Figures
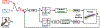


Similar articles
-
Control Aspects of Shape Memory Alloys in Robotics Applications: A Review over the Last Decade.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jun 27;22(13):4860. doi: 10.3390/s22134860. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35808360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anthropomorphic finger antagonistically actuated by SMA plates.Bioinspir Biomim. 2015 Aug 20;10(5):056002. doi: 10.1088/1748-3190/10/5/056002. Bioinspir Biomim. 2015. PMID: 26292164
-
Shape memory alloy tube actuators inherently enable internal fluidic cooling for a robotic finger under force control.Smart Mater Struct. 2020 Oct;29(11):115009. doi: 10.1088/1361-665x/ab931f. Epub 2020 Sep 22. Smart Mater Struct. 2020. PMID: 38745901 Free PMC article.
-
An Underwater Robotic Manipulator with Soft Bladders and Compact Depth-Independent Actuation.Soft Robot. 2020 Oct;7(5):535-549. doi: 10.1089/soro.2019.0087. Epub 2020 Feb 28. Soft Robot. 2020. PMID: 32109180 Free PMC article.
-
3D Printing Technologies for Flexible Tactile Sensors toward Wearable Electronics and Electronic Skin.Polymers (Basel). 2018 Jun 7;10(6):629. doi: 10.3390/polym10060629. Polymers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30966663 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Compensating the cell-induced light scattering effect in light-based bioprinting using deep learning.Biofabrication. 2021 Dec 3;14(1):10.1088/1758-5090/ac3b92. doi: 10.1088/1758-5090/ac3b92. Biofabrication. 2021. PMID: 34798629 Free PMC article.
-
Control Aspects of Shape Memory Alloys in Robotics Applications: A Review over the Last Decade.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jun 27;22(13):4860. doi: 10.3390/s22134860. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35808360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Robotic Replica of a Human Spine Uses Soft Magnetic Sensor Array to Forecast Intervertebral Loads and Posture after Surgery.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Dec 29;22(1):212. doi: 10.3390/s22010212. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35009754 Free PMC article.
-
Feeling the beat: a smart hand exoskeleton for learning to play musical instruments.Front Robot AI. 2023 Jun 29;10:1212768. doi: 10.3389/frobt.2023.1212768. eCollection 2023. Front Robot AI. 2023. PMID: 37457389 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aggarwal A, Kampmann P, Lemburg J, Kirchner F, Haptic Object Recognition in Underwater and Deep-sea Environments, Journal of field robotics, 32(2015) 167–85.
-
- Meng Q, Wang H, Li P, Wang L, He Z, Dexterous underwater robot hand: HEU Hand II, 2006 international conference on mechatronics and automation, IEEE; 2006, pp. 1477–82.
-
- Stuart HS, Bagheri M, Wang S, Barnard H, Sheng AL, Jenkins M, et al., Suction helps in a pinch: Improving underwater manipulation with gentle suction flow, 2015 IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems (IROS), IEEE; 2015, pp. 2279–84.
-
- Dahiya RS, Metta G, Valle M, Sandini G, Tactile sensing—from humans to humanoids, IEEE transactions on robotics, 26(2009) 1–20.
-
- Dennerlein J, Howe R, Shahoian E, Olroyd C, Vibrotactile feedback for an underwater telerobot, Robotics and applications; Robotic and manufacturing systems recent results in research, development and applications International symposium; 8th, Citeseer; 2000, pp. 244–9.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

