Isolation of human and murine hematopoietic stem cells for DNA damage and DNA repair assays
- PMID: 34622219
- PMCID: PMC8482037
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xpro.2021.100846
Isolation of human and murine hematopoietic stem cells for DNA damage and DNA repair assays
Abstract
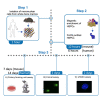
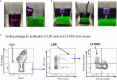
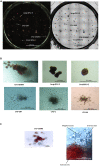
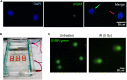
Hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs) reside in the bone marrow and supply blood cells. Efficient methods for isolation of HSPCs are required. Here, we present protocols for the isolation of human and murine HSPCs using manual and FACS-assisted techniques. Isolated HSPCs can be used for downstream applications, including colony forming unit assays and DNA damage and repair assays. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Rodríguez et al. (2021a) and (2021b).
Keywords: Cell Biology; Cell isolation; Cell-based Assays; Flow Cytometry/Mass Cytometry; Genetics; Microscopy; Stem Cells.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Healthcare workers' informal uses of mobile phones and other mobile devices to support their work: a qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Aug 27;8(8):CD015705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015705.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39189465 Free PMC article.
-
Consensus findings of an International Workshops on Genotoxicity Testing workshop on using transcriptomic biomarkers to predict genotoxicity.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2025 Jan 5. doi: 10.1002/em.22645. Online ahead of print. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2025. PMID: 39757731 Review.
-
On the objectivity, reliability, and validity of deep learning enabled bioimage analyses.Elife. 2020 Oct 19;9:e59780. doi: 10.7554/eLife.59780. Elife. 2020. PMID: 33074102 Free PMC article.
-
Depressing time: Waiting, melancholia, and the psychoanalytic practice of care.In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. In: Kirtsoglou E, Simpson B, editors. The Time of Anthropology: Studies of Contemporary Chronopolitics. Abingdon: Routledge; 2020. Chapter 5. PMID: 36137063 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Interventions to reduce harm from continued tobacco use.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Oct 13;10(10):CD005231. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005231.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27734465 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Whole-genome sequencing and mutational analysis of human cord-blood derived stem and progenitor cells.STAR Protoc. 2022 May 6;3(2):101361. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2022.101361. eCollection 2022 Jun 17. STAR Protoc. 2022. PMID: 35573477 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kiel M.J., Yilmaz O.H., Iwashita T., Yilmaz O.H., Terhorst C., Morrison S.J. SLAM family receptors distinguish hematopoietic stem and pro- genitor cells and reveal endothelial niches for stem cells. Cell. 2005;121:1109–1121. - PubMed
-
- Olive P.L., Banáth J.P. The comet assay: a method to measure DNA damage in individual cells. Nat. Protoc. 2006;1:23–29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

