In vivo Pharmacokinetic and Anticancer Studies of HH-N25, a Selective Inhibitor of Topoisomerase I, and Hormonal Signaling for Treating Breast Cancer
- PMID: 34588796
- PMCID: PMC8473721
- DOI: 10.2147/JIR.S329401
In vivo Pharmacokinetic and Anticancer Studies of HH-N25, a Selective Inhibitor of Topoisomerase I, and Hormonal Signaling for Treating Breast Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Breast cancer is the most frequently diagnosed cancer globally, and the leading cause of cancer-associated mortality among women. The efficacy of most clinical chemotherapies is often limited by poor pharmacokinetics and the development of drug resistance by tumors. In a continuing effort to explore small molecules as alternative therapies, we herein evaluated the therapeutic potential of HH-N25, a novel nitrogen-substituted anthra[1,2-c][1,2,5]thiadiazole-6,11-dione derivative.
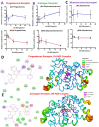
Methods: We evaluated the in vivo pharmacokinetic properties and maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of HH-N25 in rats. We also characterized the compound for in vitro and in vivo anticancer activities and its inhibitory effects against DNA topoisomerases and hormonal signaling in breast cancer. Furthermore, we used molecular docking to analyse the ligand-receptor interactions between the compound and the targets.
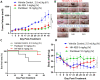
Results: The maximum serum concentration (Cmax), half-life (t1/2 beta), mean residence time (MRT), oral clearance (CL/f), and apparent volume of distribution (VD/f) of HH-N25 were 1446.67 ± 312.05 ng/mL, 4.51 ± 0.27 h, 2.56 ± 0.16 h, 8.32 ± 1.45 mL/kg/h, and 1.26 ± 0.15 mL/kg, respectively, after single-dose iv administration at 3 mg/kg body weight. HH-N25 had potent anticancer activity against a panel of human breast cancer cell lines with 50% inhibitory concentrations (IC50) ranging 0.045±0.01~4.21±0.05 µM. The drug also demonstrated marked in vivo anticancer activity at a tolerated dose and prolonged the survival duration of mice without unacceptable toxicities based on body weight changes in human tumor xenograft models. In addition, HH-N25 exhibited a dose-dependent inhibition of topoisomerase I and ligand-mediated activities of progesterone and androgen receptors.
Conclusion: HH-N25 represents a new molecular entity that selective suppressed TOP1 and hormonal signaling, and shows potent antitumor activities in human breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. HH-N25 thus represents a promising anticancer agent that warrants further preclinical and clinical exploration.
Keywords: HH-N25; anticancer activities; hormonal signaling; pharmacokinetic; topoisomerase inhibition.
© 2021 Lawal et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
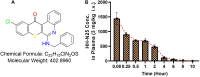


Similar articles
-
Phase I and pharmacology study of intoplicine (RP 60475; NSC 645008), novel topoisomerase I and II inhibitor, in cancer patients.Anticancer Drugs. 1996 Feb;7(2):166-74. doi: 10.1097/00001813-199602000-00004. Anticancer Drugs. 1996. PMID: 8740721 Clinical Trial.
-
In vitro and in vivo characterization of XR11576, a novel, orally active, dual inhibitor of topoisomerase I and II.Anticancer Drugs. 2002 Jan;13(1):15-28. doi: 10.1097/00001813-200201000-00002. Anticancer Drugs. 2002. PMID: 11914637
-
Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Molecular Docking Study of Cyclic Diarylheptanoids as Potential Anticancer Therapeutics.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2020;20(4):464-475. doi: 10.2174/1871520619666191125130237. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31763968
-
Overview of resistance to systemic therapy in patients with breast cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007;608:1-22. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-74039-3_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007. PMID: 17993229 Review.
-
Lopinavir/ritonavir: a review of its use in the management of HIV infection.Drugs. 2003;63(8):769-802. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200363080-00004. Drugs. 2003. PMID: 12662125 Review.
Cited by
-
Metachromin C, a marine-derived natural compound, shows potential in antitumor activity.Int J Med Sci. 2024 Oct 7;21(13):2578-2594. doi: 10.7150/ijms.101037. eCollection 2024. Int J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39439453 Free PMC article.
-
Luteolin-Rich Extract of Thespesia garckeana F. Hoffm. (Snot Apple) Contains Potential Drug-Like Candidates and Modulates Glycemic and Oxidoinflammatory Aberrations in Experimental Animals.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Jul 30;2022:1215097. doi: 10.1155/2022/1215097. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35941904 Free PMC article.
-
In silico study of novel niclosamide derivatives, SARS-CoV-2 nonstructural proteins catalytic residue-targeting small molecules drug candidates.Arab J Chem. 2023 May;16(5):104654. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2023.104654. Epub 2023 Feb 8. Arab J Chem. 2023. PMID: 36777994 Free PMC article.
-
Computational identification of novel signature of T2DM-induced nephropathy and therapeutic bioactive compounds from Azanza garckeana.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Jul 15;15(7):4504-4520. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 37560206 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of prognostic significance of cadherin (CDH) gene family in breast cancer.Aging (Albany NY). 2022 Oct 30;14(20):8498-8567. doi: 10.18632/aging.204357. Aging (Albany NY). 2022. PMID: 36315446 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–249. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I, et al. Cancer statistics for the year 2020: an overview. Int J Cancer. 2021;149(4):778–789. - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. - PubMed
-
- Chapek MA, Martindale RG. Nutrition in cancer therapy: overview for the cancer patient. J Parenteral Enteral Nutr. 2021;10:21 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

