Comparative Analysis between Urinary Calprotectin and Serum Creatinine for Early Detection of Intrinsic Acute Kidney Injury
- PMID: 34584350
- PMCID: PMC8443099
- DOI: 10.4103/ijn.IJN_83_20
Comparative Analysis between Urinary Calprotectin and Serum Creatinine for Early Detection of Intrinsic Acute Kidney Injury
Abstract
Background: Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common and important clinical condition that may lead to chronic kidney disease if it is not diagnosed and treated in its early stages. Urinary calprotectin is a valuable recognized biomarker that can be used to differentiate prerenal and intrinsic AKI. However, till date only a few reports on urine calprotectin measurement in early diagnosis of intrinsic AKI are available. In this study, we compared the sensitivity and specificity of urinary calprotectin with those of serum creatinine in detecting early intrinsic AKI.
Methods: Over 6 months period (April to October 2018), 81 of 408 patients admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit met the criteria of this cross-sectional study. Their serum creatinine and urinary calprotectin were measured on the first and third day of admission using Jaffe and Elisa radioimmunoassay methods, respectively. The AKI was defined according to the pRIFLE criteria.
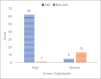
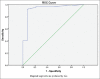
Results: Of the total 81 patients, 67 had the criteria of intrinsic AKI. Of these 62% were female and 38% were male. The mean age of the patients was 22 months. According to data analysis, the area under the curve of ROC of urinary calprotectin on day-1 to detect renal failure is 0.93 with the best cutoff point obtained at 530 ng/mL. The sensitivity, specificity, positive, and negative predictive values of urinary calprotectin levels in diagnosing AKI at this cutoff point are 92.5%, 92.8%, 98.4, and 72.2%, respectively. Besides, urinary calprotectin changes occur much earlier than the rising of serum creatinine.
Conclusion: Urinary level of calprotectin is a very sensitive biomarker for early diagnosis of intrinsic AKI in children and it can be used in intensive care units or anywhere critically ill children admitted to detect intrinsic AKI. Besides, this study shows that urine calprotectin may be a more sensitive and specific biomarker than serum creatinine in the early phases of intrinsic AKI.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; calprotectin; intrinsic AKI; serum creatinine.
Copyright: © 2021 Indian Journal of Nephrology.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflicts of interest in this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Urinary calprotectin and the distinction between prerenal and intrinsic acute kidney injury.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011 Oct;6(10):2347-55. doi: 10.2215/CJN.02490311. Epub 2011 Sep 1. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 21885792 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary Calprotectin Differentiates Between Prerenal and Intrinsic Acute Renal Allograft Failure.Transplantation. 2017 Feb;101(2):387-394. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000001124. Transplantation. 2017. PMID: 26901081
-
Urinary calprotectin, kidney injury molecule-1, and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin for the prediction of adverse outcome in pediatric acute kidney injury.Eur J Pediatr. 2017 Jun;176(6):745-755. doi: 10.1007/s00431-017-2907-y. Epub 2017 Apr 14. Eur J Pediatr. 2017. PMID: 28409285 Clinical Trial.
-
Meta-Analysis: Urinary Calprotectin for Discrimination of Intrinsic and Prerenal Acute Kidney Injury.J Clin Med. 2019 Jan 10;8(1):74. doi: 10.3390/jcm8010074. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 30634660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing the value of serum and urinary interleukins for diagnosis of acute kidney injury in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Pract Lab Med. 2022 Jan 7;28:e00262. doi: 10.1016/j.plabm.2022.e00262. eCollection 2022 Jan. Pract Lab Med. 2022. PMID: 35071719 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proficient Novel Biomarkers Guide Early Detection of Acute Kidney Injury: A Review.Diseases. 2022 Dec 30;11(1):8. doi: 10.3390/diseases11010008. Diseases. 2022. PMID: 36648873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fecal calprotectin in pediatric gastrointestinal diseases: Pros and cons.World J Clin Pediatr. 2024 Jun 9;13(2):93341. doi: 10.5409/wjcp.v13.i2.93341. eCollection 2024 Jun 9. World J Clin Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 38948001 Free PMC article.
-
The Molecular Mechanism and Therapeutic Strategy of Cardiorenal Syndrome Type 3.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Feb 6;24(2):52. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2402052. eCollection 2023 Feb. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 39077418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Biomarkers in Early Diagnosis of Acute Kidney Injury in Children.Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2022 Oct-Dec;14(4):264-269. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36504568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of Risk Factors for Perioperative Acute Kidney Injury and Management Strategies.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Dec 24;8:751793. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.751793. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 35004722 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Seibert FS, Pagonas N, Arndt R, Heller F, Dragun D, Persson P, et al. Calprotectin and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in the differentiation of pre-renal and intrinsic acute kidney injury. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2013;207:700–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous