Influence of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles on Human Health and the Environment
- PMID: 34578667
- PMCID: PMC8465434
- DOI: 10.3390/nano11092354
Influence of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles on Human Health and the Environment
Abstract
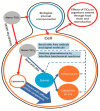
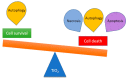
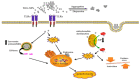
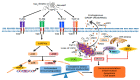
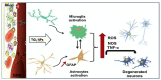
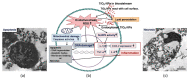
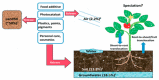
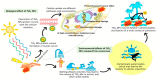
Nanotechnology has enabled tremendous breakthroughs in the development of materials and, nowadays, is well established in various economic fields. Among the various nanomaterials, TiO2 nanoparticles (NPs) occupy a special position, as they are distinguished by their high availability, high photocatalytic activity, and favorable price, which make them useful in the production of paints, plastics, paper, cosmetics, food, furniture, etc. In textiles, TiO2 NPs are widely used in chemical finishing processes to impart various protective functional properties to the fibers for the production of high-tech textile products with high added value. Such applications contribute to the overall consumption of TiO2 NPs, which gives rise to reasonable considerations about the impact of TiO2 NPs on human health and the environment, and debates regarding whether the extent of the benefits gained from the use of TiO2 NPs justifies the potential risks. In this study, different TiO2 NPs exposure modes are discussed, and their toxicity mechanisms-evaluated in various in vitro and in vivo studies-are briefly described, considering the molecular interactions with human health and the environment. In addition, in the conclusion of this study, the toxicity and biocompatibility of TiO2 NPs are discussed, along with relevant risk management strategies.
Keywords: TiO2; biocompatibility; environment; human health; oxidative stress; risk management; titanium dioxide; toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Coexistence of silver and titanium dioxide nanoparticles: enhancing or reducing environmental risks?Aquat Toxicol. 2014 Sep;154:168-75. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2014.05.020. Epub 2014 May 27. Aquat Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24907921
-
Microglial cells (BV-2) internalize titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles: toxicity and cellular responses.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016 May;23(10):9690-9. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-6190-7. Epub 2016 Feb 5. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016. PMID: 26846246
-
TiO2-NPs Toxicity and Safety: An Update of the Findings Published over the Last Six Years.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2023;23(9):1050-1057. doi: 10.2174/1389557522666220929152403. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36177628
-
Microbial synthesis of titanium dioxide nanoparticles and their importance in wastewater treatment and antimicrobial activities: a review.Front Microbiol. 2023 Oct 16;14:1270245. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1270245. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37908543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Titanium dioxide nanoparticles: some aspects of toxicity/focus on the development.Endocr Regul. 2015 Apr;49(2):97-112. doi: 10.4149/endo_2015_02_97. Endocr Regul. 2015. PMID: 25960011 Review.
Cited by
-
8-Bromo-cAMP attenuates human airway epithelial barrier disruption caused by titanium dioxide fine and nanoparticles.Tissue Barriers. 2024 Oct;12(4):2300579. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2023.2300579. Epub 2024 Jan 3. Tissue Barriers. 2024. PMID: 38166590 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles on Chick Embryo: Immunomodulatory, Hepatic and Biochemical Alterations.Vet Med Sci. 2024 Nov;10(6):e70105. doi: 10.1002/vms3.70105. Vet Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39474769 Free PMC article.
-
Inactivation of various variant types of SARS-CoV-2 by indoor-light-sensitive TiO2-based photocatalyst.Sci Rep. 2022 Apr 14;12(1):5804. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-09402-7. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35422456 Free PMC article.
-
Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticle: A Comprehensive Review on Synthesis, Applications and Toxicity.Plants (Basel). 2024 Oct 23;13(21):2964. doi: 10.3390/plants13212964. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39519883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-Criteria Decision-Making Approach for Pre-Synthesis Selection of the Optimal Physicochemical Properties of TiO2 Photocatalytic Nanoparticles for Biomedical and Environmental Applications.Molecules. 2024 Aug 6;29(16):3726. doi: 10.3390/molecules29163726. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39202805 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scharnberg A.R.D.A., de Loreto A.C., Wermuth T.B., Alves A.K., Arcaro S., dos Santos P.A.M., Rodriguez A.D.A.L. Porous ceramic supported TiO2 nanoparticles: Enhanced photocatalytic activity for Rhodamine B degradation. Boletín Soc. Española Cerám. Vidrio. 2020;59:230–238. doi: 10.1016/j.bsecv.2019.12.001. - DOI
-
- Do H.H., Nguyen D.L.T., Nguyen X.C., Le T.-H., Nguyen T.P., Trinh Q.T., Ahn S.H., Vo D.-V.N., Kim S.Y., Van Le Q. Recent progress in TiO2-based photocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction: A review. Arab. J. Chem. 2020;13:3653–3671. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2019.12.012. - DOI
-
- Hiremath V., Deonikar V.G., Kim H., Gil Seo J. Hierarchically assembled porous TiO2 nanoparticles with enhanced photocatalytic activity towards Rhodamine-B degradation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020;586:124199. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.124199. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

