C3G Protein, a New Player in Glioblastoma
- PMID: 34576182
- PMCID: PMC8466177
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms221810018
C3G Protein, a New Player in Glioblastoma
Abstract
C3G (RAPGEF1) is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for GTPases from the Ras superfamily, mainly Rap1, although it also acts through GEF-independent mechanisms. C3G regulates several cellular functions. It is expressed at relatively high levels in specific brain areas, playing important roles during embryonic development. Recent studies have uncovered different roles for C3G in cancer that are likely to depend on cell context, tumour type, and stage. However, its role in brain tumours remained unknown until very recently. We found that C3G expression is downregulated in GBM, which promotes the acquisition of a more mesenchymal phenotype, enhancing migration and invasion, but not proliferation. ERKs hyperactivation, likely induced by FGFR1, is responsible for this pro-invasive effect detected in C3G silenced cells. Other RTKs (Receptor Tyrosine Kinases) are also dysregulated and could also contribute to C3G effects. However, it remains undetermined whether Rap1 is a mediator of C3G actions in GBM. Various Rap1 isoforms can promote proliferation and invasion in GBM cells, while C3G inhibits migration/invasion. Therefore, other RapGEFs could play a major role regulating Rap1 activity in these tumours. Based on the information available, C3G could represent a new biomarker for GBM diagnosis, prognosis, and personalised treatment of patients in combination with other GBM molecular markers. The quantification of C3G levels in circulating tumour cells (CTCs) in the cerebrospinal liquid and/or circulating fluids might be a useful tool to improve GBM patient treatment and survival.
Keywords: C3G; Rap; glioblastoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
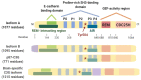

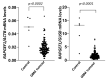

Similar articles
-
C3G downregulation induces the acquisition of a mesenchymal phenotype that enhances aggressiveness of glioblastoma cells.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Apr 6;12(4):348. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-03631-w. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 33824275 Free PMC article.
-
C3G knock-down enhances migration and invasion by increasing Rap1-mediated p38α activation, while it impairs tumor growth through p38α-independent mechanisms.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 19;7(29):45060-45078. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9911. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27286263 Free PMC article.
-
Requirement for C3G-dependent Rap1 activation for cell adhesion and embryogenesis.EMBO J. 2001 Jul 2;20(13):3333-41. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.13.3333. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11432821 Free PMC article.
-
Signalling to actin: role of C3G, a multitasking guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor.Biosci Rep. 2011 Aug;31(4):231-44. doi: 10.1042/BSR20100094. Biosci Rep. 2011. PMID: 21366540 Review.
-
[Activation of Rap1, antagonist to ras, by Crk-C3G].Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 1997 Sep;24(11):1414-21. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 1997. PMID: 9309134 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Characterization of prevalent tyrosine kinase inhibitors and their challenges in glioblastoma treatment.Front Chem. 2024 Jan 8;11:1325214. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2023.1325214. eCollection 2023. Front Chem. 2024. PMID: 38264122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New and Old Key Players in Liver Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 5;24(24):17152. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417152. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38138981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
C3G down-regulation enhances pro-migratory and stemness properties of oval cells by promoting an epithelial-mesenchymal-like process.Int J Biol Sci. 2022 Sep 25;18(15):5873-5884. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.73192. eCollection 2022. Int J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36263169 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial to Special Issue "Glioblastoma: Recapitulating the Key Breakthroughs and Future Perspective".Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 29;24(3):2548. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032548. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768870 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Louis D.N., Perry A., Reifenberger G., von Deimling A., Figarella-Branger D., Cavenee W.K., Ohgaki H., Wiestler O.D., Kleihues P., Ellison D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016;131:803–820. doi: 10.1007/s00401-016-1545-1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

