Nintedanib Regulates GRK2 and CXCR2 to Reduce Neutrophil Recruitment in Endotoxin-Induced Lung Injury
- PMID: 34576061
- PMCID: PMC8464681
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22189898
Nintedanib Regulates GRK2 and CXCR2 to Reduce Neutrophil Recruitment in Endotoxin-Induced Lung Injury
Abstract
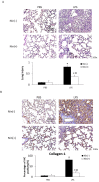
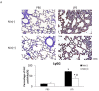
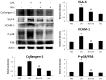
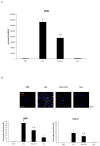
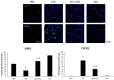
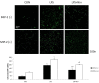
The role of nintedanib, a multiple tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in the treatment of sepsis-induced acute lung injury (ALI) remains unclear. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), also known as endotoxin, has been used to induce ALI. The goal of this study was to assess the effect of nintedanib in attenuating the histopathological changes of LPS-induced ALI. Nintedanib was administered via oral gavage to male C57BL/6 mice 24 h and 10 min before intratracheal endotoxin instillation. Lung histopathological characteristics, adhesion molecule expression, and the regulatory signaling pathways of neutrophil chemotaxis were analyzed after 24 h. We found that nintedanib significantly reduced histopathological changes and neutrophil recruitment in LPS-induced ALI. The number of neutrophils in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) was reduced in nintedanib-treated relative to untreated mice with ALI. Nintedanib mediated the downregulation of the chemotactic response to LPS by reducing the expression of adhesion molecules and the phosphorylated p38:total p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) ratio in the lungs of mice with ALI. Nintedanib also reduced the expression of lymphocyte antigen 6 complex locus G6D (Ly6G) and very late antigen 4 (VLA-4) in BALF neutrophils and mediated the downregulation of chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 2 (CXCR2) and upregulation of G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 (GRK2) activity in peripheral blood neutrophils in mice with LPS-induced ALI. Nintedanib improved the histopathological changes of LPS-induced ALI by reducing neutrophil chemotaxis. These effects were mediated by the inhibition of adhesion molecules via the activation of GRK2 and the inhibition of p38 MAPK and CXCR2.
Keywords: CXCR2; GRK2; acute lung injury; chemotaxis; neutrophil chemotaxis; nintedanib; p38 MAPK.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The main e-cigarette component vegetable glycerin enhances neutrophil migration and fibrosis in endotoxin-induced lung injury via p38 MAPK activation.Respir Res. 2023 Jan 10;24(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12931-022-02307-z. Respir Res. 2023. PMID: 36627690 Free PMC article.
-
Induced pluripotent stem cells reduce neutrophil chemotaxis via activating GRK2 in endotoxin-induced acute lung injury.Respirology. 2017 Aug;22(6):1156-1164. doi: 10.1111/resp.13053. Epub 2017 Apr 21. Respirology. 2017. PMID: 28429504
-
Nintedanib Reduces Neutrophil Chemotaxis via Activating GRK2 in Bleomycin-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 2;21(13):4735. doi: 10.3390/ijms21134735. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32630825 Free PMC article.
-
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Regulate Triggering Receptor Expressed on Myeloid Cell-1 Expression and the p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway in Endotoxin-Induced Acute Lung Injury.Stem Cells. 2019 May;37(5):631-639. doi: 10.1002/stem.2980. Epub 2019 Feb 16. Stem Cells. 2019. PMID: 30681755
-
Expanding role of CXCR2 and therapeutic potential of CXCR2 antagonists in inflammatory diseases and cancers.Eur J Med Chem. 2023 Mar 15;250:115175. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115175. Epub 2023 Feb 7. Eur J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36780833 Review.
Cited by
-
Phospholipid transfer protein ameliorates sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction through NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition.Open Med (Wars). 2024 Mar 27;19(1):20240915. doi: 10.1515/med-2024-0915. eCollection 2024. Open Med (Wars). 2024. PMID: 38584827 Free PMC article.
-
The main e-cigarette component vegetable glycerin enhances neutrophil migration and fibrosis in endotoxin-induced lung injury via p38 MAPK activation.Respir Res. 2023 Jan 10;24(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12931-022-02307-z. Respir Res. 2023. PMID: 36627690 Free PMC article.
-
GRK2 mediates cisplatin-induced acute liver injury via the modulation of NOX4.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024 Nov 15;40(1):98. doi: 10.1007/s10565-024-09940-y. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39546067 Free PMC article.
-
USP9x promotes CD8 + T-cell dysfunction in association with autophagy inhibition in septic liver injury.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2022 Nov 25;54(12):1-10. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2022174. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2022. PMID: 36514222 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

