Syzygium aromaticum Extracts as a Potential Antibacterial Inhibitors against Clinical Isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii: An In-Silico-Supported In-Vitro Study
- PMID: 34572644
- PMCID: PMC8472170
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics10091062
Syzygium aromaticum Extracts as a Potential Antibacterial Inhibitors against Clinical Isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii: An In-Silico-Supported In-Vitro Study
Abstract
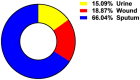
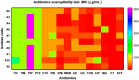
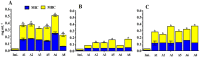
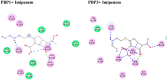
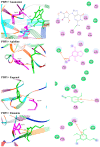
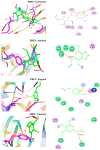
Imipenem is the most efficient antibiotic against Acinetobacter baumannii infection, but new research has shown that the organism has also developed resistance to this agent. A. baumannii isolates from a total of 110 clinical samples were identified by multiplex PCR. The antibacterial activity of Syzygium aromaticum multiple extracts was assessed following the GC-Mass spectra analysis. The molecular docking study was performed to investigate the binding mode of interactions of guanosine (Ethanolic extract compound) against Penicillin- binding proteins 1 and 3 of A. baumannii. Ten isolates of A. baumannii were confirmed to carry recA and iutA genes. Isolates were multidrug-resistant containing blaTEM and BlaSHV. The concentrations (0.04 to 0.125 mg mL-1) of S. aromaticum ethanolic extract were very promising against A. baumannii isolates. Even though imipenem (0.02 mg mL-1) individually showed a great bactericidal efficacy against all isolates, the in-silico study of guanosine, apioline, eugenol, and elemicin showed acceptable fitting to the binding site of the A. baumannii PBP1 and/or PBP3 with highest binding energy for guanosine between -7.1 and -8.1 kcal/mol respectively. Moreover, it formed π-stacked interactions with the residue ARG76 at 4.14 and 5.6, Å respectively. These findings might support the in vitro study and show a substantial increase in binding affinity and enhanced physicochemical characteristics compared to imipenem.
Keywords: GC-Mass; antibiotic-resistant genes; docking; imipenem; penicillin-binding proteins; urine samples; virulence genes; wound swab.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Efficacy of Ethanolic Extract of Syzygium aromaticum in the Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Clinical Isolates Associated with Urinary Tract Infections.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Jun 15;2021:6612058. doi: 10.1155/2021/6612058. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34221080 Free PMC article.
-
[Investigation of oxacillinase genes in nosocomial multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates by multiplex PCR and evaluation of their clonal relationship with Rep-PCR].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2015 Apr;49(2):249-58. doi: 10.5578/mb.8884. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2015. PMID: 26167825 Turkish.
-
Screening of potential lead molecules against prioritised targets of multi-drug-resistant-Acinetobacter baumannii - insights from molecular docking, molecular dynamic simulations and in vitro assays.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2019 Mar;37(5):1146-1169. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2018.1451387. Epub 2018 Mar 20. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2019. PMID: 29529934
-
[In vitro synergistic activity of sulbactam in combination with imipenem, meropenem and cefoperazone against carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii isolates].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2014 Apr;48(2):311-5. doi: 10.5578/mb.7104. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2014. PMID: 24819268 Turkish.
-
Cefiderocol: A Siderophore Cephalosporin with Activity Against Carbapenem-Resistant and Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacilli.Drugs. 2019 Feb;79(3):271-289. doi: 10.1007/s40265-019-1055-2. Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30712199 Review.
Cited by
-
Micrococcus lylae MW407006 Pigment: Production, Optimization, Nano-Pigment Synthesis, and Biological Activities.Biology (Basel). 2022 Aug 4;11(8):1171. doi: 10.3390/biology11081171. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36009797 Free PMC article.
-
An in-silico approach to target multiple proteins involved in anti-microbial resistance using natural compounds produced by wild mushrooms.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2024 Oct 21;40:101854. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2024.101854. eCollection 2024 Dec. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2024. PMID: 39498442 Free PMC article.
-
Multidrug-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Infections in the United Kingdom versus Egypt: Trends and Potential Natural Products Solutions.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Jan 1;12(1):77. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12010077. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36671278 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Algammal A.M., Hetta H.F., Batiha G.E., Hozzein W.N., El Kazzaz W.M., Hashem H.R., Tawfik A.M., El-Tarabili R.M. Virulence-determinants and antibiotic-resistance genes of MDR- E. coli isolated from secondary infections following FMD-outbreak in cattle. Sci. Rep. 2020;10:19779. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-75914-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pritsch M., Zeynudin A., Messerer M., Baumer S., Liegl G., Schubert S., Löscher T., Hoelscher M., Belachew T., Rachow A., et al. First report on bla NDM-1-producing Acinetobacter baumannii in three clinical isolates from Ethiopia. BMC Infect. Dis. 2017;17:180. doi: 10.1186/s12879-017-2289-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

