Dynamic Expression of Membrane Type 1-Matrix Metalloproteinase (Mt1-mmp/Mmp14) in the Mouse Embryo
- PMID: 34572097
- PMCID: PMC8465375
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10092448
Dynamic Expression of Membrane Type 1-Matrix Metalloproteinase (Mt1-mmp/Mmp14) in the Mouse Embryo
Abstract
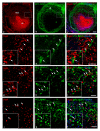
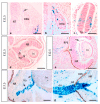
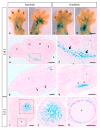
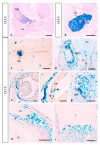
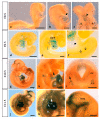
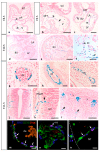
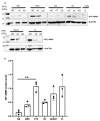
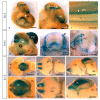
MT1-MMP/MMP14 belongs to a subgroup of the matrix metalloproteinases family that presents a transmembrane domain, with a cytosolic tail and the catalytic site exposed to the extracellular space. Deficient mice for this enzyme result in early postnatal death and display severe defects in skeletal, muscle and lung development. By using a transgenic line expressing the LacZ reporter under the control of the endogenous Mt1-mmp promoter, we reported a dynamic spatiotemporal expression pattern for Mt1-mmp from early embryonic to perinatal stages during cardiovascular development and brain formation. Thus, Mt1-mmp shows expression in the endocardium of the heart and the truncus arteriosus by E8.5, and is also strongly detected during vascular system development as well as in endothelial cells. In the brain, LacZ reporter expression was detected in the olfactory bulb, the rostral cerebral cortex and the caudal mesencephalic tectum. LacZ-positive cells were observed in neural progenitors of the spinal cord, neural crest cells and the intersomitic region. In the limb, Mt1-mmp expression was restricted to blood vessels, cartilage primordium and muscles. Detection of the enzyme was confirmed by Western blot and immunohistochemical analysis. We suggest novel functions for this metalloproteinase in angiogenesis, endocardial formation and vascularization during organogenesis. Moreover, Mt1-mmp expression revealed that the enzyme may contribute to heart, muscle and brain throughout development.
Keywords: MMP14; Mt1-mmp; angiogenesis; brain; cardiovascular development; dorsal aorta; embryo development; expression pattern; limb; metalloproteinases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Developmental expression of membrane type 4-matrix metalloproteinase (Mt4-mmp/Mmp17) in the mouse embryo.PLoS One. 2017 Sep 19;12(9):e0184767. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184767. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28926609 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between neovessels and mural cells directs the site-specific expression of MT1-MMP to endothelial tip cells.J Cell Sci. 2007 May 1;120(Pt 9):1607-14. doi: 10.1242/jcs.000679. Epub 2007 Apr 3. J Cell Sci. 2007. PMID: 17405818
-
Distinctive functions of membrane type 1 matrix-metalloprotease (MT1-MMP or MMP-14) in lung and submandibular gland development are independent of its role in pro-MMP-2 activation.Dev Biol. 2005 Jan 1;277(1):255-69. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.09.033. Dev Biol. 2005. PMID: 15572153
-
MT1-MMP and integrins: Hand-to-hand in cell communication.Biofactors. 2010 Jul-Aug;36(4):248-54. doi: 10.1002/biof.99. Biofactors. 2010. PMID: 20818710 Review.
-
MEMBRANE TYPE 1-MATRIX METALLOPROTEINASE (MT1-MMP) IDENTIFIED AS A MULTIFUNCTIONAL REGULATOR OF VASCULAR RESPONSES.Fukushima J Med Sci. 2015;61(2):91-100. doi: 10.5387/fms.2015-15. Epub 2015 Sep 11. Fukushima J Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26370683 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development of anti-membrane type 1-matrix metalloproteinase nanobodies as immunoPET probes for triple negative breast cancer imaging.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 24;9:1058455. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1058455. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36507540 Free PMC article.
-
Vanadium Modulates Proteolytic Activities and MMP-14-Like Levels during Paracentrotus lividus Embryogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 17;23(22):14238. doi: 10.3390/ijms232214238. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36430713 Free PMC article.
-
De novo disruptive heterozygous MMP21 variants are potential predisposing genetic risk factors in Chinese Han heterotaxy children.Hum Genomics. 2022 Sep 19;16(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s40246-022-00409-9. Hum Genomics. 2022. PMID: 36123719 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

