Somatostatin analog therapy effectiveness on the progression of polycystic kidney and liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
- PMID: 34559824
- PMCID: PMC8462725
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0257606
Somatostatin analog therapy effectiveness on the progression of polycystic kidney and liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
Abstract
Background: Uncertainty underlies the effectiveness of somatostatin analogues for slowing the progression of polycystic kidney or liver disease.
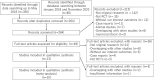
Methods: Eligible studies included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating somatostatin analog as therapy for patients with polycystic kidney disease (PKD) or polycystic liver disease (PLD) compared to placebo or standard therapy. Two reviewers independently screened studies identified from databases (MEDLINE, EMBASE, Cochrane Database), clinical trial registries, and references from pertinent articles and clinical practice guidelines. Outcome measurements were changes in total liver volume (TLV), total kidney volume (TKV), and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR).
Results: Of 264 nonduplicate studies screened, 10 RCTs met the inclusion criteria. The body of evidence provided estimates warranting moderate confidence. Meta-analysis of 7 RCTs including a total of 652 patients showed that somatostatin analogs are associated with a lower %TLV growth rate compared to control (mean difference, -6.37%; 95% CI -7.90 to -4.84, p<0.00001), and with a lower %TKV growth rate compared to control (mean difference, -3.66%; 95% CI -5.35 to -1.97, p<0.0001). However, it was not associated with a difference in eGFR decline (mean difference, -0.96 mL/min./1.73m2; 95% CI -2.38 to 0.46, p = 0.19).
Conclusions: Current body of evidence suggests that somatostatin analogs therapy slows the increase rate of TLV and TKV in patients with PKD or PLD compared to control within a 3-year follow-up period. It does not seem to have an effect on the change in eGFR. Somatostatin analogs therapy can be a promising treatment for ADPKD or ADPLD, and we need to continue to research its effectiveness for ADPKD or ADPLD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-acting somatostatin analogue treatments in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease and polycystic liver disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMJ Open. 2020 Jan 9;10(1):e032620. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-032620. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 31924636 Free PMC article.
-
Pansomatostatin Agonist Pasireotide Long-Acting Release for Patients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney or Liver Disease with Severe Liver Involvement: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020 Sep 7;15(9):1267-1278. doi: 10.2215/CJN.13661119. Epub 2020 Aug 25. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32843370 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Somatostatin analog therapy for severe polycystic liver disease: results after 2 years.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012 Sep;27(9):3532-9. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfs152. Epub 2012 Jul 6. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012. PMID: 22773240 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Lanreotide and its Potential Applications in Polycystic Kidney and Liver Diseases.Curr Top Med Chem. 2015;16(2):133-40. doi: 10.2174/1568026615666150701115157. Curr Top Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 26126910 Review.
-
Treatments to slow progression of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials.Nephrology (Carlton). 2014 Apr;19(4):217-26. doi: 10.1111/nep.12211. Nephrology (Carlton). 2014. PMID: 24460701 Review.
Cited by
-
Drugs in Clinical Development to Treat Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease.Drugs. 2022 Jul;82(10):1095-1115. doi: 10.1007/s40265-022-01745-9. Epub 2022 Jul 19. Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35852784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcatheter arterial embolization therapy in patients with polycystic kidney disease and liver disease: review from case series.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2025 Jan;29(1):29-38. doi: 10.1007/s10157-024-02597-1. Epub 2024 Nov 20. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39565471 Review.
-
Evidence of nonsurgical treatment for polycystic liver disease.Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2022 Jul 21;13:20406223221112563. doi: 10.1177/20406223221112563. eCollection 2022. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2022. PMID: 35898920 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of SEC61A1 mutant R236C in two patient-derived cellular platforms.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 25;14(1):9506. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-59033-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38664472 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolism-based approaches for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Feb 16;10:1126055. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1126055. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36876046 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous