SPAAC Pulse-Chase: A Novel Click Chemistry-Based Method to Determine the Half-Life of Cellular Proteins
- PMID: 34557490
- PMCID: PMC8452969
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2021.722560
SPAAC Pulse-Chase: A Novel Click Chemistry-Based Method to Determine the Half-Life of Cellular Proteins
Abstract
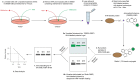
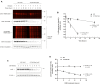
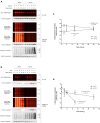
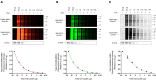
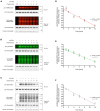
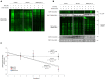
Assessing the stability and degradation of proteins is central to the study of cellular biological processes. Here, we describe a novel pulse-chase method to determine the half-life of cellular proteins that overcomes the limitations of other commonly used approaches. This method takes advantage of pulse-labeling of nascent proteins in living cells with the bioorthogonal amino acid L-azidohomoalanine (AHA) that is compatible with click chemistry-based modifications. We validate this method in both mammalian and yeast cells by assessing both over-expressed and endogenous proteins using various fluorescent and chemiluminescent click chemistry-compatible probes. Importantly, while cellular stress responses are induced to a limited extent following live-cell AHA pulse-labeling, we also show that this response does not result in changes in cell viability and growth. Moreover, this method is not compromised by the cytotoxicity evident in other commonly used protein half-life measurement methods and it does not require the use of radioactive amino acids. This new method thus presents a versatile, customizable, and valuable addition to the toolbox available to cell biologists to determine the stability of cellular proteins.
Keywords: SPAAC; click chemistry; mammalian cells; protein half-life; protein stability and degradation; pulse-chase analysis; yeast.
Copyright © 2021 Morey, Esmaeili, Duennwald and Rylett.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Measuring Protein Synthesis during Cell Cycle by Azidohomoalanine (AHA) Labeling and Flow Cytometric Analysis.Bio Protoc. 2019 Apr 20;9(8):e3215. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3215. eCollection 2019 Apr 20. Bio Protoc. 2019. PMID: 33655007 Free PMC article.
-
Nonradioactive quantification of autophagic protein degradation with L-azidohomoalanine labeling.Nat Protoc. 2017 Dec;12(2):279-288. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2016.160. Epub 2017 Jan 12. Nat Protoc. 2017. PMID: 28079880
-
A high-throughput-compatible assay to measure the degradation of endogenous Huntingtin proteins.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2016 Sep;37(10):1307-1314. doi: 10.1038/aps.2016.31. Epub 2016 Jun 6. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2016. PMID: 27264314 Free PMC article.
-
Specific and quantitative labeling of biomolecules using click chemistry.Front Physiol. 2014 Nov 24;5:457. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00457. eCollection 2014. Front Physiol. 2014. PMID: 25505421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Click chemistry and bioorthogonal reactions: unprecedented selectivity in the labeling of biological molecules.Biochemistry. 2009 Jul 21;48(28):6571-84. doi: 10.1021/bi9007726. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19485420 Review.
Cited by
-
IL-2Rα KO mice exhibit maternal microchimerism and reveal nuclear localization of IL-2Rα in lymphoid and non-lymphoid cells.Front Immunol. 2024 May 15;15:1369818. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1369818. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38812502 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of site-specifically labelled fluorescent human XPA to investigate DNA binding dynamics during nucleotide excision repair.Methods. 2024 Apr;224:47-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2024.02.006. Epub 2024 Feb 20. Methods. 2024. PMID: 38387709
-
Engineered Proteins and Materials Utilizing Residue-Specific Noncanonical Amino Acid Incorporation.Chem Rev. 2024 Aug 14;124(15):9113-9135. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.3c00855. Epub 2024 Jul 15. Chem Rev. 2024. PMID: 39008623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular turnover and degradation of the most common missense cystathionine beta-synthase variants causing homocystinuria.Protein Sci. 2024 Aug;33(8):e5123. doi: 10.1002/pro.5123. Protein Sci. 2024. PMID: 39041895 Free PMC article.
-
Labeling strategies to track protozoan parasite proteome dynamics.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2023 Aug;75:102316. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2023.102316. Epub 2023 May 14. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2023. PMID: 37192562 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abreu-Villaca Y., Filgueiras C. C., Manhaes A. C. (2011). Developmental aspects of the cholinergic system. Behav. Brain Res. 221 367–378. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

