Antiviral Effectivity of Favipiravir Against Peste Des Petits Ruminants Virus Is Mediated by the JAK/STAT and PI3K/AKT Pathways
- PMID: 34552976
- PMCID: PMC8450531
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2021.722840
Antiviral Effectivity of Favipiravir Against Peste Des Petits Ruminants Virus Is Mediated by the JAK/STAT and PI3K/AKT Pathways
Abstract
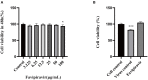
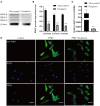
Peste des petits ruminants virus (PPRV), belonging to the genus Morbillivirus in the family Paramyxoviridae, causes severe infectious disease in small ruminants and has been rapidly spreading in many parts of Africa, the Middle East, and Asia. Although vaccination is considered to be an effective means of controlling PPR, the heat-sensitive nature of the vaccines against PPRV greatly limits their application in areas with a hot climate. In the present study, we investigated the anti-PPRV effects of favipiravir and sought to identify the underlying mechanisms in vitro using the Vero cell line. MTT assays, Western blotting, indirect immunofluorescence assays, virus plaque formation assays, and qRT-PCR were used to assess the effects of favipiravir on the life cycle of PPRV and the expression of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). Additionally, the expression levels of JAK1, STAT1, phosphorylated (p)-STAT1, PI3K, AKT, and p-AKT, as well as those of signaling molecules acting downstream of the JAK/STAT and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways, were determined by Western blotting and qRT-PCR. The results indicated that, in PPRV-infected, favipiravir-treated Vero cells, the attachment, invasion, replication, and release of PPRV were significantly inhibited, as was the expression of RdRp, when compared with that in untreated PPRV-infected cells. Furthermore, in favipiravir-treated cells, the expression of JAK1 and STAT1 was downregulated, whereas that of p-STAT1 was significantly upregulated. Similarly, the expression levels of PKR, IRF9, ISG54, and MxA proteins that are associated with innate antiviral activity in host cells were also markedly increased. Moreover, with favipiravir treatment, the expression of PI3K and p-AKT and the p-AKT/AKT ratio were significantly decreased, whereas the expression of AKT was noticeably upregulated. The expression of GSK3, NF-κB p65, p-NF-κB p65, and BAD was also increased with favipiravir treatment, while the expression of CREB, p-CREB, p-GSK3, and Bcl-2 was slightly decreased. In addition, all the p-GSK3/GSK3, p-CREB/CREB, p-NF-κB/NF-κB, and p-BAD/BAD ratios were significantly reduced in favipiravir-treated cells. These results implied that the antiviral effectivity of favipiravir against PPRV is mediated by the JAK/STAT and PI3K/AKT pathways and that favipiravir has potential for use as an effective antiviral agent against PPRV.
Keywords: antiviral activity; favipiravir; peste des petits ruminants virus; ruminants; signal pathway.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang, Deng, Liu, Chen, Liu and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ribavirin inhibits peste des petits ruminants virus proliferation in vitro.Vet Med (Praha). 2023 Dec 26;68(12):464-476. doi: 10.17221/56/2023-VETMED. eCollection 2023 Dec. Vet Med (Praha). 2023. PMID: 38303996 Free PMC article.
-
The Nucleoprotein and Phosphoprotein of Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus Inhibit Interferons Signaling by Blocking the JAK-STAT Pathway.Viruses. 2019 Jul 8;11(7):629. doi: 10.3390/v11070629. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31288481 Free PMC article.
-
Peste des petits ruminants virus non-structural C protein inhibits the induction of interferon-β by potentially interacting with MAVS and RIG-I.Virus Genes. 2021 Feb;57(1):60-71. doi: 10.1007/s11262-020-01811-y. Epub 2021 Jan 3. Virus Genes. 2021. PMID: 33389635 Free PMC article.
-
Review of Peste des Petits Ruminants Occurrence and Spread in Tanzania.Animals (Basel). 2021 Jun 7;11(6):1698. doi: 10.3390/ani11061698. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34200290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expanding Diversity of Susceptible Hosts in Peste Des Petits Ruminants Virus Infection and Its Potential Mechanism Beyond.Front Vet Sci. 2020 Feb 28;7:66. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00066. eCollection 2020. Front Vet Sci. 2020. PMID: 32181263 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fuzhengjiedu San inhibits porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway.PLoS One. 2024 May 6;19(5):e0283728. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0283728. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38709810 Free PMC article.
-
Peste des petits ruminants virus infection induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis via IRE1-XBP1 and IRE1-JNK signaling pathways.J Vet Sci. 2024 Mar;25(2):e21. doi: 10.4142/jvs.23236. J Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 38568823 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rojas JM, Moreno H, Valcárcel F, Peña L, Sevilla N, Martín V. Vaccination with recombinant adenoviruses expressing the peste des petits ruminants virus F or H proteins overcomes viral immunosuppression and induces protective immunity against PPRV challenge in sheep. PLoS One. (2014) 9:e101226–32. 10.1371/journal.pone.0101226 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

