Evidence and Potential Mechanisms of Jin-Gui Shen-Qi Wan as a Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 34552482
- PMCID: PMC8450514
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.699932
Evidence and Potential Mechanisms of Jin-Gui Shen-Qi Wan as a Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
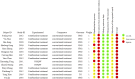
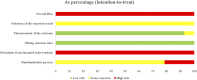
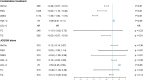
Background: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a subtype of diabetes mellitus characterized by progressive dysfunction of β-cell insulin secretion and insulin resistance. Jīn-Guì Shèn-Qì Wán (JGSQW) has for many years been widely used in clinical practice as a treatment for T2DM. However, its effect remains unknown. Objectives: This study aims to summarize the clinical evidence of the effect of JGSQW on glucose and lipid metabolism in T2DM and the potential mechanisms underlying this effect. Methods: Six databases were searched without language or publication status restrictions. Data were extracted to a predefined template for synthesis. Results: Fourteen studies with 1586 participants were included in this meta-analysis. All 14 studies were judged to be at high risk of bias. JGSQW is safe for T2DM patients. Pooled results indicated that combination treatment results in a reduction in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) (mean difference (MD) -0.49%; 95% CI -0.67 to -0.31), fasting blood glucose (FBG) (MD -0.84; 95% CI -1.19 to -0.49), and 2-hour postprandial glucose 2hBG (MD -1.38; 95% CI -1.60 to -1.16). No significant difference in glucose metabolism was observed between JGSQW and hypoglycemic agents. The available evidence was insufficient to determine the effects on lipid metabolism. Sensitivity analyses indicated that these results were robust. Conclusion: By combining the available evidence, we found that JGSQW is safe for T2DM patients. Compared with hypoglycemic agents alone, combination treatment with JGSQW enhances the effect on glucose metabolism in patients with T2DM. We found no difference in the efficacy of JGSQW alone compared to hypoglycemic agents alone. In terms of lipid metabolism, the current evidence is insufficient and too inconsistent for us to draw firm conclusions, so further studies are needed.
Keywords: Jin-Gui Shen-Qi Wan; meta-analysis; systematic review; traditional Chinese medicine; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Copyright © 2021 Hu, Liu and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Jin-Gui-Shen-Qi Wan alleviates fibrosis in mouse diabetic nephropathy via MHC class II.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Apr 24;324:117745. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.117745. Epub 2024 Jan 14. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38228231
-
Jin Gui Shen Qi Wan, a traditional Chinese medicine, alleviated allergic airway hypersensitivity and inflammatory cell infiltration in a chronic asthma mouse model.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Dec 5;227:181-190. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.08.028. Epub 2018 Aug 30. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30172058
-
The efficacy and safety of dachaihu decoction in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 8;13:918681. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.918681. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36003504 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness of traditional Chinese medicine-based lifestyle interventions on biomedical, psychosocial, and behavioral outcomes in individuals with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review with meta-analysis.Int J Nurs Stud. 2018 Apr;80:165-180. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2018.01.009. Epub 2018 Feb 19. Int J Nurs Stud. 2018. PMID: 29471267 Review.
-
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Versus Medical Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Obese Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Apr;95(17):e3462. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003462. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27124041 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role and Mechanisms of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Airway Inflammation and Remodeling in Asthma: Overview and Progress.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 15;13:917256. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.917256. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35910345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Application of Traditional Chinese Medicine Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Evidence Map.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jul 19;2022:2755332. doi: 10.1155/2022/2755332. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35911140 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ShenQiWan ameliorates renal injury in type 2 diabetic mice by modulating mitochondrial fusion and endoplasmic reticulum stress.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Nov 10;14:1265551. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1265551. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38026991 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical observations and mechanistic insights of traditional Chinese medicine in the management of diabetic retinopathy.Pharm Biol. 2024 Dec;62(1):529-543. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2024.2369292. Epub 2024 Jun 26. Pharm Biol. 2024. PMID: 38921697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of Crude, Diverse, and Multiple Advanced Glycation End-Product Patterns May Be Important and Beneficial.Metabolites. 2023 Dec 19;14(1):3. doi: 10.3390/metabo14010003. Metabolites. 2023. PMID: 38276293 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bin J. (2020). Clinical Effect of Modified Jingui Shenqi Pill on Diabetic Nephropathy of Yin Yang Deficiency Type. J. Clin. rational Drug use 13, 58–59.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources