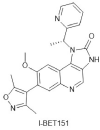
Anticancer Effects of I-BET151, an Inhibitor of Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal Domain Proteins
- PMID: 34540687
- PMCID: PMC8443787
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2021.716830
Anticancer Effects of I-BET151, an Inhibitor of Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal Domain Proteins
Abstract
I-BET151 is an inhibitor of bromodomain and extra-terminal domain (BET) proteins that selectively inhibits BET family members (BRD2, BRD3, BRD4, and BRDT). Over the past ten years, many studies have demonstrated the potential of I-BET151 in cancer treatment. Specifically, I-BET151 causes cell cycle arrest and inhibits tumor cell proliferation in some hematological malignancies and solid tumors, such as breast cancer, glioma, melanoma, neuroblastoma, and ovarian cancer. The anticancer activity of I-BET151 is related to its effects on NF-κB, Notch, and Hedgehog signal transduction pathway, tumor microenvironment (TME) and telomere elongation. Remarkably, the combination of I-BET151 with select anticancer drugs can partially alleviate the occurrence of drug resistance in chemotherapy. Especially, the combination of forskolin, ISX9, CHIR99021, I-BET151 and DAPT allows GBM cells to be reprogrammed into neurons, and this process does not experience an intermediate pluripotent state. The research on the anticancer mechanism of I-BET151 will lead to new treatment strategies for clinical cancer.
Keywords: I-BET151; bromodomain and extra-terminal domain protein; cancer; drug combination; signal transduction.
Copyright © 2021 Lai, Liu, Zhao, Ma and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
BET bromodomain proteins are required for glioblastoma cell proliferation.Epigenetics. 2014 Apr;9(4):611-20. doi: 10.4161/epi.27906. Epub 2014 Feb 19. Epigenetics. 2014. PMID: 24496381 Free PMC article.
-
NF-κB signaling activation via increases in BRD2 and BRD4 confers resistance to the bromodomain inhibitor I-BET151 in U937 cells.Leuk Res. 2018 Nov;74:57-63. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2018.09.016. Epub 2018 Oct 2. Leuk Res. 2018. PMID: 30300821
-
The BET bromodomain inhibitor I-BET151 acts downstream of smoothened protein to abrogate the growth of hedgehog protein-driven cancers.J Biol Chem. 2014 Dec 19;289(51):35494-502. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.595348. Epub 2014 Oct 29. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25355313 Free PMC article.
-
The Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal Domain (BET) Family: Functional Anatomy of BET Paralogous Proteins.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Nov 7;17(11):1849. doi: 10.3390/ijms17111849. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27827996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal (BET) Domain Protein Inhibitors for Solid Tumor Cancers.J Immunother Precis Oncol. 2020 Feb 5;3(1):16-22. doi: 10.4103/JIPO.JIPO_2_20. eCollection 2020 Feb. J Immunother Precis Oncol. 2020. PMID: 35756176 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of Histone Modifications and Their Therapeutic Targeting in Hematological Malignancies.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 7;23(21):13657. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113657. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. Retraction in: Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 28;25(7):3762. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073762 PMID: 36362442 Free PMC article. Retracted. Review.
-
BRD4: an effective target for organ fibrosis.Biomark Res. 2024 Aug 30;12(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s40364-024-00641-6. Biomark Res. 2024. PMID: 39215370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Modulation of Gremlin-1/NOTCH Pathway in Experimental Crescentic Immune-Mediated Glomerulonephritis.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Jan 20;15(2):121. doi: 10.3390/ph15020121. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35215234 Free PMC article.
-
Protein acylation: mechanisms, biological functions and therapeutic targets.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Dec 29;7(1):396. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01245-y. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 36577755 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro cytotoxicity of Withania somnifera (L.) roots and fruits on oral squamous cell carcinoma cell lines: a study supported by flow cytometry, spectral, and computational investigations.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 18;15:1325272. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1325272. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38303989 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

