Plasma Lipolysis and Changes in Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid Signaling Lipids Reveal Abnormal Lipid Metabolism in Chronic Migraine
- PMID: 34531722
- PMCID: PMC8438335
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.691733
Plasma Lipolysis and Changes in Plasma and Cerebrospinal Fluid Signaling Lipids Reveal Abnormal Lipid Metabolism in Chronic Migraine
Abstract
Background: Lipids are a primary storage form of energy and the source of inflammatory and pain signaling molecules, yet knowledge of their importance in chronic migraine (CM) pathology is incomplete. We aim to determine if plasma and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) lipid metabolism are associated with CM pathology.
Methods: We obtained plasma and CSF from healthy controls (CT, n = 10) or CM subjects (n = 15) diagnosed using the International Headache Society criteria. We measured unesterified fatty acid (UFA) and esterified fatty acids (EFAs) using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Glycerophospholipids (GP) and sphingolipid (SP) levels were determined using LC-MS/MS, and phospholipase A2 (PLA2) activity was determined using fluorescent substrates.
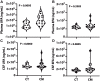
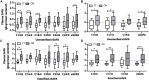
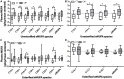
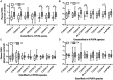
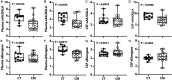
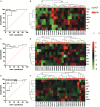
Results: Unesterified fatty acid levels were significantly higher in CM plasma but not in CSF. Unesterified levels of five saturated fatty acids (SAFAs), eight monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs), five ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), and five ω-6 PUFAs are higher in CM plasma. Esterified levels of three SAFAs, eight MUFAs, five ω-3 PUFAs, and three ω-6 PUFAs, are higher in CM plasma. The ratios C20:4n-6/homo-γ-C20:3n-6 representative of delta-5-desaturases (D5D) and the elongase ratio are lower in esterified and unesterified CM plasma, respectively. In the CSF, the esterified D5D index is lower in CM. While PLA2 activity was similar, the plasma UFA to EFA ratio is higher in CM. Of all plasma GP/SPs detected, only ceramide levels are lower (p = 0.0003) in CM (0.26 ± 0.07%) compared to CT (0.48 ± 0.06%). The GP/SP proportion of platelet-activating factor (PAF) is significantly lower in CM CSF.
Conclusions: Plasma and CSF lipid changes are consistent with abnormal lipid metabolism in CM. Since plasma UFAs correspond to diet or adipose tissue levels, higher plasma fatty acids and UFA/EFA ratios suggest enhanced adipose lipolysis in CM. Differences in plasma and CSF desaturases and elongases suggest altered lipid metabolism in CM. A lower plasma ceramide level suggests reduced de novo synthesis or reduced sphingomyelin hydrolysis. Changes in CSF PAF suggest differences in brain lipid signaling pathways in CM. Together, this pilot study shows lipid metabolic abnormality in CM corresponding to altered energy homeostasis. We propose that controlling plasma lipolysis, desaturases, elongases, and lipid signaling pathways may relieve CM symptoms.
Keywords: chronic migraine; insulin resistance; lipases; lipid signaling; lipolysis; metabolic syndrome; phospholipase A2; platelet-activating factor.
Copyright © 2021 Castor, Dawlaty, Arakaki, Gross, Woldeamanuel, Harrington, Cowan and Fonteh.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Human cerebrospinal fluid fatty acid levels differ between supernatant fluid and brain-derived nanoparticle fractions, and are altered in Alzheimer's disease.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 23;9(6):e100519. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100519. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24956173 Free PMC article.
-
Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Composition of Cerebrospinal Fluid Fractions Shows Their Contribution to Cognitive Resilience of a Pre-symptomatic Alzheimer's Disease Cohort.Front Physiol. 2020 Feb 14;11:83. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00083. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32116789 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma fatty acid abnormality in Sudanese drug-resistant epileptic patients.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2021 Apr;167:102271. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2021.102271. Epub 2021 Mar 24. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 2021. PMID: 33798873
-
"Cell Membrane Theory of Senescence" and the Role of Bioactive Lipids in Aging, and Aging Associated Diseases and Their Therapeutic Implications.Biomolecules. 2021 Feb 8;11(2):241. doi: 10.3390/biom11020241. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33567774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Omega-3 fatty acids and adipose tissue function in obesity and metabolic syndrome.Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2015 Sep;121(Pt A):24-41. doi: 10.1016/j.prostaglandins.2015.07.003. Epub 2015 Jul 26. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2015. PMID: 26219838 Review.
Cited by
-
Biomarkers of Migraine: An Integrated Evaluation of Preclinical and Clinical Findings.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 10;24(6):5334. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065334. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Microbiota-Dependent Treatment of Wuzhuyu Decoction for Chronic Migraine Model Rat Associated with Anxiety-Depression Like Behavior.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023 Jan 6;2023:2302653. doi: 10.1155/2023/2302653. eCollection 2023. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023. PMID: 36647428 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomics profiling reveals mitochondrial damage in the thalamus in a mouse model of chronic migraine.J Headache Pain. 2023 Sep 5;24(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s10194-023-01646-6. J Headache Pain. 2023. PMID: 37667199 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of Amino Acid, Lipid, and Acylpyruvate Metabolism in Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension: A Non-targeted Case Control and Longitudinal Metabolomic Study.J Proteome Res. 2023 Apr 7;22(4):1127-1137. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.2c00449. Epub 2022 Dec 19. J Proteome Res. 2023. PMID: 36534069 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying causal genes for migraine by integrating the proteome and transcriptome.J Headache Pain. 2023 Aug 17;24(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s10194-023-01649-3. J Headache Pain. 2023. PMID: 37592229 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abdelmagid S. A., Clarke S. E., Roke K., Nielsen D. E., Badawi A., El-Sohemy A., et al. (2015). Ethnicity, sex, FADS genetic variation, and hormonal contraceptive use influence delta-5- and delta-6-desaturase indices and plasma docosahexaenoic acid concentration in young Canadian adults: a cross-sectional study. Nutr. Metab. 12:14. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

