Mutagenicity of carcinogenic heterocyclic amines in Salmonella typhimurium YG strains and transgenic rodents including gpt delta
- PMID: 34526143
- PMCID: PMC8444484
- DOI: 10.1186/s41021-021-00207-0
Mutagenicity of carcinogenic heterocyclic amines in Salmonella typhimurium YG strains and transgenic rodents including gpt delta
Abstract
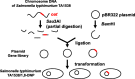
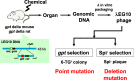
Chemical carcinogens to humans have been usually identified by epidemiological studies on the relationships between occupational or environmental exposure to the agents and specific cancer induction. In contrast, carcinogenic heterocyclic amines were identified under the principle that mutagens in bacterial in the Ames test are possible human carcinogens. In the 1970s to 1990s, more than 10 heterocyclic amines were isolated from pyrolysates of amino acids, proteins, meat or fish as mutagens in the Ames test, and they were demonstrated as carcinogens in rodents. In the 1980s and 1990s, we have developed derivatives of the Ames tester strains that overexpressed acetyltransferase of Salmonella typhimurium. These strains such as Salmonella typhimurium YG1024 exhibited a high sensitivity to the mutagenicity of the carcinogenic heterocyclic amines. Because of the high sensitivity, YG1024 and other YG strains were used for various purposes, e.g., identification of novel heterocyclic amines, mechanisms of metabolic activation, comparison of mutagenic potencies of various heterocyclic amines, and the co-mutagenic effects. In the 1990s and 2000s, we developed transgenic mice and rats for the detection of mutagenicity of chemicals in vivo. The transgenics were generated by the introduction of reporter genes for mutations into fertilized eggs of mice and rats. We named the transgenics as gpt delta because the gpt gene of Escherichia coli was used for detection of point mutations such as base substitutions and frameshifts and the red/gam genes of λ phage were employed to detect deletion mutations. The transgenic rodents gpt delta and other transgenics with lacI or lacZ as reporter genes have been utilized for characterization of mutagenicity of heterocyclic amines in vivo. In this review, we summarized the in vitro mutagenicity of heterocyclic amines in Salmonella typhimurium YG strains and the in vivo mutagenicity in transgenic rodents. We discussed the relationships between in vitro and in vivo mutagenicity of the heterocyclic amines and their relations to the carcinogenicity.
Keywords: Acetyltransferase; Ames test; Carcinogenicity; Heterocyclic amines; Mutagenicity; Salmonella typhimurium YG strains; Transgenic; gpt delta.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
My career development with Ames test: A personal recollection.Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2019 Nov;847:503095. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2019.503095. Epub 2019 Sep 18. Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 2019. PMID: 31699345
-
The mutagenicity of amino-derivatives of diphenyl ether herbicides in new Salmonella typhimurium YG tester strains.Water Sci Technol. 2002;46(11-12):395-400. Water Sci Technol. 2002. PMID: 12523784
-
Assay of 855 test chemicals in ten tester strains using a new modification of the Ames test for bacterial mutagens.Cancer Res. 1979 Mar;39(3):682-93. Cancer Res. 1979. PMID: 371791
-
Heterocyclic amines: Mutagens/carcinogens produced during cooking of meat and fish.Cancer Sci. 2004 Apr;95(4):290-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2004.tb03205.x. Cancer Sci. 2004. PMID: 15072585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Food-derived mutagens and carcinogens.Cancer Res. 1992 Apr 1;52(7 Suppl):2092s-2098s. Cancer Res. 1992. PMID: 1544146 Review.
Cited by
-
High-throughput screening of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome for 2-amino-3-methylimidazo [4,5-f] quinoline resistance identifies colon cancer-associated genes.G3 (Bethesda). 2023 Dec 6;13(12):jkad219. doi: 10.1093/g3journal/jkad219. G3 (Bethesda). 2023. PMID: 37738679 Free PMC article.
-
The Toxicological Assessment of Anoectochilus burmannicus Ethanolic-Extract-Synthesized Selenium Nanoparticles Using Cell Culture, Bacteria, and Drosophila melanogaster as Suitable Models.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Oct 22;13(20):2804. doi: 10.3390/nano13202804. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37887954 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-Endpoint Toxicological Assessment of Chrysin Loaded Oil-in-Water Emulsion System in Different Biological Models.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024 Jun 8;14(12):1001. doi: 10.3390/nano14121001. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38921877 Free PMC article.
-
Chemoinformatic Design and Profiling of Derivatives of Dasabuvir, Efavirenz, and Tipranavir as Potential Inhibitors of Zika Virus RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase and Methyltransferase.ACS Omega. 2022 Sep 6;7(37):33330-33348. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.2c03945. eCollection 2022 Sep 20. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 36157724 Free PMC article.
-
The inhibition effect and mechanism of typical hydrocolloids on the formation of heterocyclic amines: A study based on quantum chemical computation analysis.Curr Res Food Sci. 2024 Sep 21;9:100862. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2024.100862. eCollection 2024. Curr Res Food Sci. 2024. PMID: 39416363 Free PMC article.
References
-
- IARC. IARC monographs on the identification of carcinogenic hazards to humans. Lyon: WHO Press. Available from: https://monographs.iarc.who.int/agents-classified-by-the-iarc/
-
- IARC . Asbestos. Arsenic, fibre, metal and dusts, a review of human carcinogens. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risks of Chemicals to Humans. 100C. Lyon: WHO Press; 2012. pp. 219–310.
-
- IARC . 1,2-dichloropropane. Some chemicals used as solvents and in polymer manufacture. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. 110. WHO Press; 2017. pp. 141–176.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

