High-Level Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Concentration Is Closely Associated With an Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 34513950
- PMCID: PMC8427036
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.705273
High-Level Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Concentration Is Closely Associated With an Increased Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
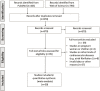
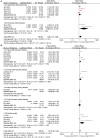
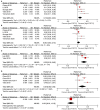
Background: The association between fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) and cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk remains unclear. We conducted this systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the association between FGF21 and CVDs, and relevant vascular parameters. Methods: PubMed and Web of Science databases were systematically searched to identify relevant studies published before March 2021. The FGF21 concentration was compared between individuals with and without CVDs. The effect of FGF21 on CVD risk was assessed by using hazard ratio (HR) and odds ratio (OR). The association between FGF21 and vascular parameters was assessed by Pearson's r. Study quality was assessed using Newcastle-Ottawa Scale and Joanna Briggs Institution Checklist. Results: A total of 29,156 individuals from 30 studies were included. Overall, the serum FGF21 concentration was significantly higher in CVD patients (p < 0.001), especially for coronary artery disease (CAD) (p < 0.001) and hypertension (p < 0.001). The pooled OR (p = 0.009) and HR (p < 0.001) showed that the risk of CVDs increased with FGF21. The linear association between FGF21 and vascular parameters, including pulse wave velocity (r = 0.32), carotid intima-media thickness (r = 0.21), ankle-brachial index (r = 0.33), systolic blood pressure (r = 0.13), and diastolic blood pressure (r = 0.05), was insignificant. The incidence of overall CVDs (p = 0.03) was significantly higher in individuals with higher FGF21 levels. Conclusion: High-level serum FGF21 concentration is closely associated with an increased risk of CVDs, which may be independent of vascular parameters. A standard FGF21 classification threshold needs to be established before clinical use for CVD risk assessment. Systematic Review Registration:https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?RecordID=241968, identifier: CRD42021241968.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; coronary heart disease; fibroblast growth factor 21; hypertension; meta-analysis; risk factor.
Copyright © 2021 Zhang, Yan, Yang, Qian, Nie, Yang, Yan, Wei, Ruan, Huang, Zhang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Close association between lifestyle and circulating FGF21 levels: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 25;13:984828. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.984828. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36093108 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship of fibroblast growth factor 21 with subclinical atherosclerosis and cardiovascular events: Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis.Atherosclerosis. 2019 Aug;287:46-53. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2019.06.898. Epub 2019 Jun 8. Atherosclerosis. 2019. PMID: 31212234
-
Serum fibroblast growth factor-21 levels are associated with carotid atherosclerosis independent of established cardiovascular risk factors.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013 Oct;33(10):2454-9. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.301599. Epub 2013 Jul 25. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23887638
-
Plasma Albumin and Incident Cardiovascular Disease: Results From the CGPS and an Updated Meta-Analysis.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020 Feb;40(2):473-482. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.313681. Epub 2019 Dec 19. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020. PMID: 31852221 Review.
-
Physiological and Pharmacological Roles of FGF21 in Cardiovascular Diseases.J Diabetes Res. 2016;2016:1540267. doi: 10.1155/2016/1540267. Epub 2016 May 9. J Diabetes Res. 2016. PMID: 27247947 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Connecting the Dots: FGF21 as a Potential Link between Obesity and Cardiovascular Health in Acute Coronary Syndrome Patients.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Aug 3;46(8):8512-8525. doi: 10.3390/cimb46080501. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39194718 Free PMC article.
-
Serum FGF21 Levels Predict the MACE in Patients With Myocardial Infarction After Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Apr 6;9:850517. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.850517. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35463746 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 and Total Testosterone in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Men With Coronary Heart Disease.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 15;13:912243. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.912243. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35909513 Free PMC article.
-
Close association between lifestyle and circulating FGF21 levels: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 25;13:984828. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.984828. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36093108 Free PMC article.
-
The Nuanced Metabolic Functions of Endogenous FGF21 Depend on the Nature of the Stimulus, Tissue Source, and Experimental Model.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jan 3;12:802541. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.802541. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35046901 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs) . Available online at: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-disea... (accessed June 11, 2021).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

