Upregulation of miR-144-3p expression attenuates glioma cell viability and invasion by targeting BCL6
- PMID: 34504602
- PMCID: PMC8393981
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2021.10591
Upregulation of miR-144-3p expression attenuates glioma cell viability and invasion by targeting BCL6
Abstract
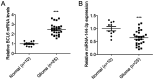
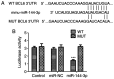
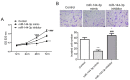
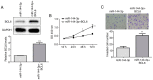
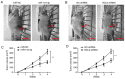
Glioma remains to be an aggressive type of cancer with poor prognosis irrespective of the type of standard treatment applied. Therefore, identification of accurate early diagnostic methods and therapeutic strategies for glioma is imperative for the treatment of this disease. The expression of a number of miRNAs in glioma have been reported to be associated with the regulation of tumorigenic progression, cancer cell proliferation, metastasis, invasion, angiogenesis and drug resistance. The aim of the present study was to assess the function of the microRNA (miR/miRNA)-144-3p/BCL6 axis in glioma. Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR was used to measure miR-144-3p and BCL6 expression. Western blotting was used for measuring BCL6 expression. Luciferase reporter assay was used to assess the association between miR-144-3p and BCL6 and a tumor xenograft model was established for assess tumor growth. The data demonstrated that miR-144-3p was decreased whereas BCL6 expression was increased in glioma tissues compared with those in healthy human brain tissues, where miR-144-3p suppressed BCL6 expression by targeting the 3'-UTR sequence of BCL6. miR-144-3p overexpression alleviated proliferation and invasion in U251 cells whereas transfection with the BCL6-overexpressing plasmid rescued the suppressive effects of miR-144-3p upregulation on the proliferation and invasion of U251 cells. In addition, miR-144-3p overexpression and BCL6 downregulation inhibited tumor progression in a mouse tumor xenograft model. The present findings suggest that miR-144-3p and BCL6 may serve to be indicator of proliferation and invasion for patients with glioma. Furthermore, BCL6 may serve an important role in the miR-144-3p-mediated regulation of proliferation and invasion of glioma cells, where the miR-144-3p/BCL6 axis can be used to target patients with glioma therapeutically.
Keywords: BCL6; glioma; invasion; microRNA-144-3p; viability.
Copyright © 2020, Spandidos Publications.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
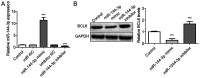
Similar articles
-
Transcription factor SP1-induced microRNA-146b-3p facilitates the progression and metastasis of colorectal cancer via regulating FAM107A.Life Sci. 2021 Jul 15;277:119398. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119398. Epub 2021 Apr 5. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33831429
-
MicroRNA-423-3p promotes glioma growth by targeting PANX2.Oncol Lett. 2018 Jul;16(1):179-188. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8636. Epub 2018 May 4. Oncol Lett. 2018. Retraction in: Oncol Lett. 2021 Aug;22(2):572. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12833. PMID: 29928399 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Overexpression of XIST facilitates cell proliferation, invasion and suppresses cell apoptosis by reducing radio-sensitivity of glioma cells via miR-329-3p/CREB1 axis.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020 Mar;24(6):3190-3203. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202003_20686. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32271437
-
miR-494-3p Regulates Cellular Proliferation, Invasion, Migration, and Apoptosis by PTEN/AKT Signaling in Human Glioblastoma Cells.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2015 Jul;35(5):679-87. doi: 10.1007/s10571-015-0163-0. Epub 2015 Feb 8. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 25662849 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA homeobox (HOX) A11-AS promotes malignant progression of glioma by targeting miR-124-3p.Neoplasma. 2018;65(4):505-514. doi: 10.4149/neo_2018_170705N462. Neoplasma. 2018. PMID: 30064227
Cited by
-
B Cell Lymphoma 6 (BCL6): A Conserved Regulator of Immunity and Beyond.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 11;25(20):10968. doi: 10.3390/ijms252010968. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456751 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
