Multivalent electrostatic pi-cation interaction between synaptophysin and synapsin is responsible for the coacervation
- PMID: 34496937
- PMCID: PMC8424992
- DOI: 10.1186/s13041-021-00846-y
Multivalent electrostatic pi-cation interaction between synaptophysin and synapsin is responsible for the coacervation
Abstract
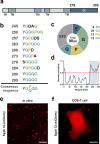
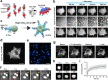
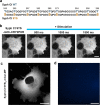
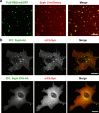
We recently showed that synaptophysin (Syph) and synapsin (Syn) can induce liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS) to cluster small synaptic-like microvesicles in living cells which are highly reminiscent of SV cluster. However, as there is no physical interaction between them, the underlying mechanism for their coacervation remains unknown. Here, we showed that the coacervation between Syph and Syn is primarily governed by multivalent pi-cation electrostatic interactions among tyrosine residues of Syph C-terminal (Ct) and positively charged Syn. We found that Syph Ct is intrinsically disordered and it alone can form liquid droplets by interactions among themselves at high concentration in a crowding environment in vitro or when assisted by additional interactions by tagging with light-sensitive CRY2PHR or subunits of a multimeric protein in living cells. Syph Ct contains 10 repeated sequences, 9 of them start with tyrosine, and mutating 9 tyrosine to serine (9YS) completely abolished the phase separating property of Syph Ct, indicating tyrosine-mediated pi-interactions are critical. We further found that 9YS mutation failed to coacervate with Syn, and since 9YS retains Syph's negative charge, the results indicate that pi-cation interactions rather than simple charge interactions are responsible for their coacervation. In addition to revealing the underlying mechanism of Syph and Syn coacervation, our results also raise the possibility that physiological regulation of pi-cation interactions between Syph and Syn during synaptic activity may contribute to the dynamics of synaptic vesicle clustering.
Keywords: Liquid–liquid phase separation (LLPS); Pi–cation interactions; Presynaptic nerve terminals; Synapsin; Synaptic vesicle cluster; Synaptophysin.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cooperative function of synaptophysin and synapsin in the generation of synaptic vesicle-like clusters in non-neuronal cells.Nat Commun. 2021 Jan 11;12(1):263. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-20462-z. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33431828 Free PMC article.
-
Vesicle Clustering in a Living Synapse Depends on a Synapsin Region that Mediates Phase Separation.Cell Rep. 2020 Feb 25;30(8):2594-2602.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.01.092. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 32101738
-
The Phosphoprotein Synapsin Ia Regulates the Kinetics of Dense-Core Vesicle Release.J Neurosci. 2021 Mar 31;41(13):2828-2841. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2593-19.2021. Epub 2021 Feb 25. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33632727 Free PMC article.
-
Synapsin I, synapsin II, and synaptophysin: marker proteins of synaptic vesicles.Brain Pathol. 1993 Jan;3(1):87-95. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.1993.tb00729.x. Brain Pathol. 1993. PMID: 7903586 Review.
-
Charge block-driven liquid-liquid phase separation - mechanism and biological roles.J Cell Sci. 2024 Jun 1;137(11):jcs261394. doi: 10.1242/jcs.261394. Epub 2024 Jun 10. J Cell Sci. 2024. PMID: 38855848 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuronal biomolecular condensates and their implications in neurodegenerative diseases.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Mar 24;15:1145420. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1145420. eCollection 2023. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37065458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
α-Synuclein in the Synaptic Vesicle Liquid Phase: Active Player or Passive Bystander?Front Mol Biosci. 2022 May 18;9:891508. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.891508. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35664678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cross-Talk of Cation-π Interactions with Electrostatic and Aromatic Interactions: A Salt-Dependent Trade-off in Biomolecular Condensates.J Phys Chem Lett. 2023 Sep 28;14(38):8460-8469. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.3c01642. Epub 2023 Sep 18. J Phys Chem Lett. 2023. PMID: 37721444 Free PMC article.
-
Overlapping role of synaptophysin and synaptogyrin family proteins in determining the small size of synaptic vesicles.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Jul 16;121(29):e2409605121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2409605121. Epub 2024 Jul 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 38985768 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

