ACBD3 modulates KDEL receptor interaction with PKA for its trafficking via tubulovesicular carrier
- PMID: 34493279
- PMCID: PMC8424950
- DOI: 10.1186/s12915-021-01137-7
ACBD3 modulates KDEL receptor interaction with PKA for its trafficking via tubulovesicular carrier
Abstract
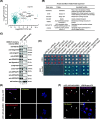
Background: KDEL receptor helps establish cellular equilibrium in the early secretory pathway by recycling leaked ER-chaperones to the ER during secretion of newly synthesized proteins. Studies have also shown that KDEL receptor may function as a signaling protein that orchestrates membrane flux through the secretory pathway. We have recently shown that KDEL receptor is also a cell surface receptor, which undergoes highly complex itinerary between trans-Golgi network and the plasma membranes via clathrin-mediated transport carriers. Ironically, however, it is still largely unknown how KDEL receptor is distributed to the Golgi at steady state, since its initial discovery in late 1980s.
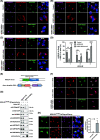
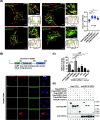
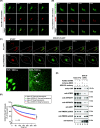
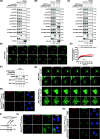
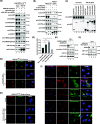
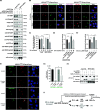
Results: We used a proximity-based in vivo tagging strategy to further dissect mechanisms of KDEL receptor trafficking. Our new results reveal that ACBD3 may be a key protein that regulates KDEL receptor trafficking via modulation of Arf1-dependent tubule formation. We demonstrate that ACBD3 directly interact with KDEL receptor and form a functionally distinct protein complex in ArfGAPs-independent manner. Depletion of ACBD3 results in re-localization of KDEL receptor to the ER by inducing accelerated retrograde trafficking of KDEL receptor. Importantly, this is caused by specifically altering KDEL receptor interaction with Protein Kinase A and Arf1/ArfGAP1, eventually leading to increased Arf1-GTP-dependent tubular carrier formation at the Golgi.
Conclusions: These results suggest that ACBD3 may function as a negative regulator of PKA activity on KDEL receptor, thereby restricting its retrograde trafficking in the absence of KDEL ligand binding. Since ACBD3 was originally identified as PAP7, a PBR/PKA-interacting protein at the Golgi/mitochondria, we propose that Golgi-localization of KDEL receptor is likely to be controlled by its interaction with ACBD3/PKA complex at steady state, providing a novel insight for establishment of cellular homeostasis in the early secretory pathway.
Keywords: ACBD3; Arf1-GTP; ArfGAPs; Golgi; KDEL receptor; Protein Kinase A.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
KDEL Receptor Trafficking to the Plasma Membrane Is Regulated by ACBD3 and Rab4A-GTP.Cells. 2023 Apr 4;12(7):1079. doi: 10.3390/cells12071079. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37048152 Free PMC article.
-
An A-kinase anchoring protein (ACBD3) coordinates traffic-induced PKA activation at the Golgi.J Biol Chem. 2023 May;299(5):104696. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.104696. Epub 2023 Apr 10. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37044218 Free PMC article.
-
KDEL receptor is a cell surface receptor that cycles between the plasma membrane and the Golgi via clathrin-mediated transport carriers.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Feb;78(3):1085-1100. doi: 10.1007/s00018-020-03570-3. Epub 2020 Jun 19. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 32562023 Free PMC article.
-
Acyl-coenzyme A binding domain containing 3 (ACBD3; PAP7; GCP60): an emerging signaling molecule.Prog Lipid Res. 2010 Jul;49(3):218-34. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2009.12.003. Epub 2010 Jan 4. Prog Lipid Res. 2010. PMID: 20043945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of Golgi signaling and trafficking by the KDEL receptor.Histochem Cell Biol. 2013 Oct;140(4):395-405. doi: 10.1007/s00418-013-1130-9. Epub 2013 Jul 20. Histochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23873287 Review.
Cited by
-
Recruitment of PI4KIIIβ to the Golgi by ACBD3 is dependent on an upstream pathway of a SNARE complex and golgins.Mol Biol Cell. 2024 Feb 1;35(2):ar20. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E23-09-0376. Epub 2023 Dec 22. Mol Biol Cell. 2024. PMID: 38134218 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of ACBD3 as a new molecular biomarker in pan-cancers through bioinformatic analysis: a preclinical study.Eur J Med Res. 2023 Dec 14;28(1):590. doi: 10.1186/s40001-023-01576-8. Eur J Med Res. 2023. PMID: 38098097 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between KDEL receptor and EGF receptor mediates cell proliferation and migration via STAT3 signaling.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Feb 20;22(1):140. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01517-w. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38378560 Free PMC article.
-
N-terminal acetyltransferase 6 facilitates enterovirus 71 replication by regulating PI4KB expression and replication organelle biogenesis.J Virol. 2024 Feb 20;98(2):e0174923. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01749-23. Epub 2024 Jan 8. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 38189249 Free PMC article.
-
KDEL Receptors: Pathophysiological Functions, Therapeutic Options, and Biotechnological Opportunities.Biomedicines. 2022 May 25;10(6):1234. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10061234. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35740256 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

