Downregulation of let-7 by Electrical Acupuncture Increases Protein Synthesis in Mice
- PMID: 34489723
- PMCID: PMC8417904
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2021.697139
Downregulation of let-7 by Electrical Acupuncture Increases Protein Synthesis in Mice
Abstract
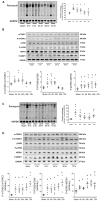
Background: Our previous study found that acupuncture with low frequency electrical stimulation (Acu/LFES) prevents muscle atrophy by attenuation of protein degradation in mice. The current study examines the impact of Acu/LFES on protein synthesis.
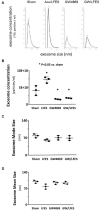
Method: C57/BL6 mice received Acu/LFES treatment on hindlimb for 30 min once. Acu/LFES points were selected by WHO Standard Acupuncture Nomenclature and electric stimulation applied using an SDZ-II Electronic acupuncture instrument. Muscle protein synthesis was measured by the surface-sensing of translation (SUnSET) assay. Exosomes were isolated using serial centrifugation and concentration and size of the collected exosomes were measured using a NanoSight instrument. The mature microRNA library in serum exosomes was validated using a High Sensitivity DNA chip.
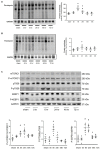
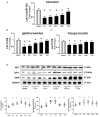
Results: Protein synthesis was enhanced in the both hindlimb and forelimb muscles. Blocking exosome secretion with GW4869 decreased the Acu/LFES-induced increases in protein synthesis. MicroRNA-deep sequencing demonstrated that four members of the Let-7 miRNA family were significantly decreased in serum exosomes. Real time qPCR further verified Acu/LFES-mediated decreases of let-7c-5p in serum exosomes and skeletal muscles. In cultured C2C12 myotubes, inhibition of let-7c not only increased protein synthesis, but also enhanced protein abundance of Igf1 and Igf1 receptors. Using a luciferase reporter assay, we demonstrated that let-7 directly inhibits Igf1.
Conclusion: Acu/LFES on hindlimb decreases let-7-5p leading to upregulation of the Igf1 signaling and increasing protein synthesis in both hindlimb and forelimb skeletal muscles. This provides a new understanding of how the electrical acupuncture treatment can positively influence muscle health.
Keywords: Acu/LFES; IGF-1 signaling; exosome; mTOR; microRNA; skeletal muscle.
Copyright © 2021 Huang, Yu, Kuma, Klein, Wang, Hassounah, Cai and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Electroacupuncture Promotes Skeletal Muscle Myogenic Differentiation and Protein Synthesis by Reducing Let-7c-5p Levels.Altern Ther Health Med. 2024 Jan;30(1):472-480. Altern Ther Health Med. 2024. PMID: 37820679
-
Electrically stimulated acupuncture increases renal blood flow through exosome-carried miR-181.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018 Dec 1;315(6):F1542-F1549. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00259.2018. Epub 2018 Aug 22. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30132347 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture plus low-frequency electrical stimulation (Acu-LFES) attenuates denervation-induced muscle atrophy.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2016 Feb 15;120(4):426-36. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00175.2015. Epub 2015 Dec 17. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2016. PMID: 26679610 Free PMC article.
-
PI3 kinase regulation of skeletal muscle hypertrophy and atrophy.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010;346:267-78. doi: 10.1007/82_2010_78. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20593312 Review.
-
Acupuncture and Related Therapies for the Cognitive Function of Alzheimer's Disease: A Network Meta-Analysis.Iran J Public Health. 2021 Dec;50(12):2411-2426. doi: 10.18502/ijph.v50i12.7924. Iran J Public Health. 2021. PMID: 36317033 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
chi-miR-99b-3p Regulates the Proliferation of Goat Skeletal Muscle Satellite Cells In Vitro by Targeting Caspase-3 and NCOR1.Animals (Basel). 2022 Sep 11;12(18):2368. doi: 10.3390/ani12182368. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139227 Free PMC article.
-
Low-frequency electrical stimulation alleviates immobilization-evoked disuse muscle atrophy by repressing autophagy in skeletal muscle of rabbits.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022 Apr 28;23(1):398. doi: 10.1186/s12891-022-05350-5. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022. PMID: 35484550 Free PMC article.
-
An electrical stimulation intervention protocol to prevent disuse atrophy and muscle strength decline: an experimental study in rat.J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2023 Jun 29;20(1):84. doi: 10.1186/s12984-023-01208-6. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2023. PMID: 37386493 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA profiling of B16F10 melanoma cell exosomes reveals melanin synthesis-related genes.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 29;10(9):e30474. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30474. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38711645 Free PMC article.
-
The CX-DZ-II intelligent electronic stimulator for neck pain caused by cervical spondylosis: A two-center, randomized, controlled, and non-inferiority trial.Front Neurosci. 2022 Jul 28;16:910574. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.910574. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35968361 Free PMC article.
References
-
- D’Souza R. F., Zeng N., Figueiredo V. C., Markworth J. F., Durainayagam B. R., Mitchell S. M., et al. (2018). Dairy protein supplementation modulates the human skeletal muscle microRNA response to lower limb immobilization. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 62:e1701028. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

