Determination role of some biomarkers tests for severe SARS-COV-2 infections in babylon province/IRAQ
- PMID: 34485097
- PMCID: PMC8397530
- DOI: 10.1016/j.matpr.2021.08.225
Determination role of some biomarkers tests for severe SARS-COV-2 infections in babylon province/IRAQ
Abstract
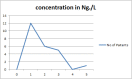
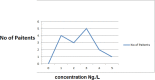
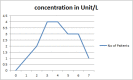
In a series of 30 SARS-COV-2 infected patients whom clinically proven as severe pulmonary infection form. These were found with male/female ratio of 1:1. The age range of below 50 years old account for 60% and those of above 50 years old constitute the remaining 40%. They were the residents of Merjan Teaching Hospital/ Babylon Province/Iraq, to the period of March to April 2021 and primary screen by PCR for Sars-cov-2 RNA genes, in public health central laboratory found to be positive. The over- all laboratory investigation were; D -dimer, Ferritin, LDH, acute phase reactant C, and IL6. LDH was tempted to probe the immune mediated pulmonary tissue injury (367.48 U/L.), ferritin response may indicate hemolytic and acute phase reactant expressed as hyper-inflammation (331.1 ng/L.). |The D-dimer shed a light on the fibrino-lytic responses (6049 ng/L.) post to the immune-thrombotic overreactions, where IL6 levels give a clue to the state of hyper-cytokinemia (171.92 pg/L.). The overall immune status of these patients was as; Hyper-inflammatory and immune overreaction. The inflammatory and immune herd plots were of skewed distribution types.
Keywords: D-dimer; Ferritin; Hyper-cytokinemia; Inflammation; LDH.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. Selection and peer-review under responsibility of the scientific committee of the International Conference on Recent Advances in Mechanical Engineering and Nanomaterials.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Study of the D-dimer, C-reactive protein, and autoantibodies markers among HBV infected patients in Babylon province, Iraq.Biomedicine (Taipei). 2021 Dec 1;11(4):67-72. doi: 10.37796/2211-8039.1186. eCollection 2021. Biomedicine (Taipei). 2021. PMID: 35223421 Free PMC article.
-
[Clinical features and risk factors for secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in elderly patients with severe SARS-CoV-2 infection: a multicenter retrospective cohort study].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023 Aug;35(8):793-799. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20230510-00158. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023. PMID: 37593855 Chinese.
-
Sarilumab versus standard of care for the early treatment of COVID-19 pneumonia in hospitalized patients: SARTRE: a structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Sep 16;21(1):794. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04633-3. Trials. 2020. PMID: 32938496 Free PMC article.
-
The COVIRL002 Trial-Tocilizumab for management of severe, non-critical COVID-19 infection: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Sep 3;21(1):758. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04680-w. Trials. 2020. PMID: 32883328 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 and Sepsis.Turk J Med Sci. 2021 Dec 17;51(SI-1):3301-3311. doi: 10.3906/sag-2108-239. Turk J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 34590796 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- C.H. Sudre, et al. Six distinct types of covid-19 identified, symptom cluster in covid-19: a potential clinical prediction tool from covid-19 symptom study group.doi.org/ 101191/ 2020.00.1220056.
-
- Staff M. Covid-19 long term effect. Myoclinic. 2020
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous