Insulin/IGF-1 signaling promotes immunosuppression via the STAT3 pathway: impact on the aging process and age-related diseases
- PMID: 34476533
- PMCID: PMC8572812
- DOI: 10.1007/s00011-021-01498-3
Insulin/IGF-1 signaling promotes immunosuppression via the STAT3 pathway: impact on the aging process and age-related diseases
Abstract
Background: The insulin/IGF-1 signaling pathway has a major role in the regulation of longevity both in Caenorhabditis elegans and mammalian species, i.e., reduced activity of this pathway extends lifespan, whereas increased activity accelerates the aging process. The insulin/IGF-1 pathway controls protein and energy metabolism as well as the proliferation and differentiation of insulin/IGF-1-responsive cells. Insulin/IGF-1 signaling also regulates the functions of the innate and adaptive immune systems. The purpose of this review was to elucidate whether insulin/IGF-1 signaling is linked to immunosuppressive STAT3 signaling which is known to promote the aging process.
Methods: Original and review articles encompassing the connections between insulin/IGF-1 and STAT3 signaling were examined from major databases including Pubmed, Scopus, and Google Scholar.
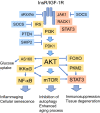
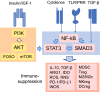
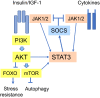
Results: The activation of insulin/IGF-1 receptors stimulates STAT3 signaling through the JAK and AKT-driven signaling pathways. STAT3 signaling is a major activator of immunosuppressive cells which are able to counteract the chronic low-grade inflammation associated with the aging process. However, the activation of STAT3 signaling stimulates a negative feedback response through the induction of SOCS factors which not only inhibit the activity of insulin/IGF-1 receptors but also that of many cytokine receptors. The inhibition of insulin/IGF-1 signaling evokes insulin resistance, a condition known to be increased with aging. STAT3 signaling also triggers the senescence of both non-immune and immune cells, especially through the activation of p53 signaling.
Conclusions: Given that cellular senescence, inflammaging, and counteracting immune suppression increase with aging, this might explain why excessive insulin/IGF-1 signaling promotes the aging process.
Keywords: Ageing; Alzheimer’s; FoxO; Immunosenescence; Tolerance; mTOR.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
JAK/STAT3 pathway is involved in survival of neurons in response to insulin-like growth factor and negatively regulated by suppressor of cytokine signaling-3.J Biol Chem. 2005 Sep 9;280(36):31830-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M501316200. Epub 2005 Jul 5. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15998644
-
RhoA, Rho kinase, JAK2, and STAT3 may be the intracellular determinants of longevity implicated in the progeric influence of obesity: Insulin, IGF-1, and leptin may all conspire to promote stem cell exhaustion.Med Hypotheses. 2006;66(3):570-6. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2005.09.008. Epub 2005 Oct 14. Med Hypotheses. 2006. PMID: 16226846
-
Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signal transduction and the Janus Kinase/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (JAK-STAT) pathway.Biofactors. 2009 Jan-Feb;35(1):76-81. doi: 10.1002/biof.20. Biofactors. 2009. PMID: 19319849 Review.
-
Insulin-like growth factor-1 regulates the SIRT1-p53 pathway in cellular senescence.Aging Cell. 2014 Aug;13(4):669-78. doi: 10.1111/acel.12219. Epub 2014 Apr 30. Aging Cell. 2014. PMID: 25070626 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the Molecular Mechanism of Immunosenescence in Drosophila.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Aug 21;19(9):2472. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092472. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30134574 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Increased circulating monocyte MDSCs positively correlate with serum Interleukin-10 in metastatic melanoma patients.Innate Immun. 2023 Apr;29(3-4):37-44. doi: 10.1177/17534259231172079. Epub 2023 May 9. Innate Immun. 2023. PMID: 37160888 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in the mammary gland during aging and its links with breast diseases.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2023 May 15;55(6):1001-1019. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2023073. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2023. PMID: 37184281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes of Signaling Pathways in Hypothalamic Neurons with Aging.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Oct 12;45(10):8289-8308. doi: 10.3390/cimb45100523. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37886966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterizing the Tumor Microenvironment and Its Prognostic Impact in Breast Cancer.Cells. 2024 Sep 10;13(18):1518. doi: 10.3390/cells13181518. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39329702 Free PMC article.
-
Hydroxytyrosol Interference with Inflammaging via Modulation of Inflammation and Autophagy.Nutrients. 2023 Apr 5;15(7):1774. doi: 10.3390/nu15071774. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37049611 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

