Gene and Biochemical Pathway Evaluation of Burns Injury via Protein-Protein Interaction Network Analysis
- PMID: 34466480
- PMCID: PMC8344118
- DOI: 10.31661/gmj.v8i0.1257
Gene and Biochemical Pathway Evaluation of Burns Injury via Protein-Protein Interaction Network Analysis
Abstract
Background: Severe burns injury can affect several vital systems in the body and can cause inflammation in organs such as the heart, liver, and kidney. Many inflammatory mediators and regulatory hormones related to burn injuries are recognized. In this study, the genes related to burn injury interacted via network analysis, and the central nodes were enriched through gene ontology (GO).
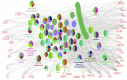
Materials and methods: Disease query of STRING database was used for data gathering, and the network was constructed using Cytoscape software version 3.6.0. After gene screening, the central nodes were enriched via GO analysis by ClueGO. The highlighted genes and pathways were clustered and analyzed in detail.
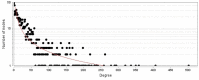
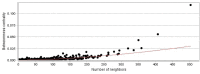
Results: Among 1067 genes, 35 critical genes that are involved in the 14 highlighted biochemical pathways were recognized. Interpretation of the finding indicates that a number of central genes can be considered as potential biomarkers related to burn injury.
Conclusion: Can we revise to "Burn injuries have features that are common to several diseases and increases their risk.
Keywords: Biochemical Pathway; Biomarker; Burn; Gene; Protein-Protein Interaction Network.
Copyright© 2019, Galen Medical Journal.
Similar articles
-
Biochemical pathway analysis of gastric atrophy.Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2018 Spring;11(2):118-124. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2018. PMID: 29910852 Free PMC article.
-
Gene screening of colorectal cancers via network analysis.Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2019 Spring;12(2):149-154. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2019. PMID: 31191840 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of an immunorelated protein-protein interaction network for clarifying the mechanism of burn.Burns. 2016 Mar;42(2):405-13. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2015.06.015. Epub 2015 Dec 29. Burns. 2016. PMID: 26739088
-
[Screening genes related with leukocyte responses early after burn injury: analysis of differentially gene expression profiling data in mice].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2015 Dec;35(12):1775-81. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2015. PMID: 26714915 Chinese.
-
Exploration of the mechanism of Zisheng Shenqi decoction against gout arthritis using network pharmacology.Comput Biol Chem. 2021 Feb;90:107358. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107358. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Comput Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33243703 Review.
Cited by
-
The Highlighted Role of GAPDH and Nitric-Oxide Synthase Regulator Activity in Proton Beam Irradiated Melanoma BLM Cells.J Lasers Med Sci. 2019 Fall;10(Suppl 1):S68-S72. doi: 10.15171/jlms.2019.S13. Epub 2019 Dec 1. J Lasers Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 32021677 Free PMC article.
-
Side effects of omeprazole: a system biology study.Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2021 Fall;14(4):334-341. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2021. PMID: 34659661 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Post-Radiation Time Effect on Gene Expression Profiles of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Samples After Appling a UV Laser.J Lasers Med Sci. 2021 Dec 30;12:e91. doi: 10.34172/jlms.2021.91. eCollection 2021. J Lasers Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 35155176 Free PMC article.
-
Network analysis of liver cancer: a system biology approach.Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2023;16(3):319-325. doi: 10.22037/ghfbb.v16i2.2514. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2023. PMID: 37767318 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aulick LH, Wilmore DW, Mason Jr A, Pruitt Jr B. Influence of the burn wound on peripheral circulation in thermally injured patients. Am J Physiol. 1977;233(4):H520–26. - PubMed
-
- Herndon D, Abston S, Stein M. Increased thromboxane B2 levels in the plasma of burned and septic burned patients. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1984;159(3):210–3. - PubMed
-
- Morykwas MJ, David LR, Schneider AM, Whang C, Jennings DA, Canty C. et al. Use of subatmospheric pressure to prevent progression of partial-thickness burns in a swine model. J Burn Care Rehabil. 1999;20(suppl_1_pt_1):15–21. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources