Cancer associated mutations in Sec61γ alter the permeability of the ER translocase
- PMID: 34460824
- PMCID: PMC8439465
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009780
Cancer associated mutations in Sec61γ alter the permeability of the ER translocase
Abstract
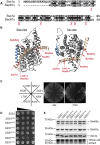
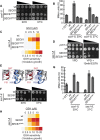
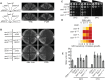
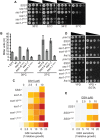
Translocation of secretory and integral membrane proteins across or into the ER membrane occurs via the Sec61 complex, a heterotrimeric protein complex possessing two essential sub-units, Sec61p/Sec61α and Sss1p/Sec61γ and the non-essential Sbh1p/Sec61β subunit. In addition to forming a protein conducting channel, the Sec61 complex maintains the ER permeability barrier, preventing flow of molecules and ions. Loss of Sec61 integrity is detrimental and implicated in the progression of disease. The Sss1p/Sec61γ C-terminus is juxtaposed to the key gating module of Sec61p/Sec61α and is important for gating the translocon. Inspection of the cancer genome database identifies six mutations in highly conserved amino acids of Sec61γ/Sss1p. We identify that five out of the six mutations identified affect gating of the ER translocon, albeit with varying strength. Together, we find that mutations in Sec61γ that arise in malignant cells result in altered translocon gating dynamics, this offers the potential for the translocon to represent a target in co-therapy for cancer treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The conserved C-terminus of Sss1p is required to maintain the endoplasmic reticulum permeability barrier.J Biol Chem. 2020 Feb 14;295(7):2125-2134. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.010378. Epub 2019 Dec 17. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 31848225 Free PMC article.
-
Sss1p is required to complete protein translocon activation.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 15;285(42):32671-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.128256. Epub 2010 Aug 13. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20709746 Free PMC article.
-
The transmembrane domain is sufficient for Sbh1p function, its association with the Sec61 complex, and interaction with Rtn1p.J Biol Chem. 2007 Oct 19;282(42):30618-28. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M701840200. Epub 2007 Aug 14. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17699516 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging View on the Molecular Functions of Sec62 and Sec63 in Protein Translocation.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 25;22(23):12757. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312757. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functions and Mechanisms of the Human Ribosome-Translocon Complex.Subcell Biochem. 2019;93:83-141. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-28151-9_4. Subcell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31939150 Review.
Cited by
-
The endoplasmic reticulum membrane protein Sec62 as potential therapeutic target in SEC62 overexpressing tumors.Front Physiol. 2022 Oct 3;13:1014271. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1014271. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36262254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibitors of the Sec61 Complex and Novel High Throughput Screening Strategies to Target the Protein Translocation Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 5;22(21):12007. doi: 10.3390/ijms222112007. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769437 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

