A peptidic inhibitor for PD-1 palmitoylation targets its expression and functions
- PMID: 34458782
- PMCID: PMC8341464
- DOI: 10.1039/d0cb00157k
A peptidic inhibitor for PD-1 palmitoylation targets its expression and functions
Abstract
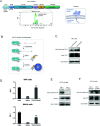
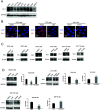
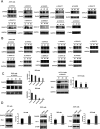
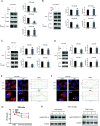
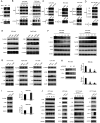
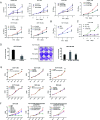
Programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) is a crucial anticancer target, but the relatively low response rate and acquired resistance to existing antibody drugs highlight an urgent need to develop alternative targeting strategies. Here, we report the palmitoylation of PD-1, discover the main DHHC enzyme for this modification, reveal the mechanism of its effect on PD-1 protein stability, and rationally develop a peptide for targeting PD-1 expression. Palmitoylation promoted the trafficking of PD-1 to the recycling endosome, thus preventing its lysosome-dependent degradation. Palmitoylation of PD-1, but not of PD-L1, promoted mTOR signaling and tumor cell proliferation, and targeting palmitoylation displayed significant anti-tumor effects in a three-dimensional culture system. A peptide was designed to competitively inhibit PD-1 palmitoylation and expression, opening a new route for developing PD-1 inhibitors and combinatorial cancer immunotherapy.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest related to this work. Data and material availability: all data needed to evaluate the conclusions in the paper are present in the paper or the ESI.† The plasmids require a material transfer agreement from Fudan University, China.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Study and analysis of antitumor resistance mechanism of PD1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint blocker.Cancer Med. 2020 Nov;9(21):8086-8121. doi: 10.1002/cam4.3410. Epub 2020 Sep 2. Cancer Med. 2020. PMID: 32875727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HIP1R targets PD-L1 to lysosomal degradation to alter T cell-mediated cytotoxicity.Nat Chem Biol. 2019 Jan;15(1):42-50. doi: 10.1038/s41589-018-0161-x. Epub 2018 Nov 5. Nat Chem Biol. 2019. PMID: 30397328
-
Inhibiting PD-L1 palmitoylation enhances T-cell immune responses against tumours.Nat Biomed Eng. 2019 Apr;3(4):306-317. doi: 10.1038/s41551-019-0375-6. Epub 2019 Mar 25. Nat Biomed Eng. 2019. PMID: 30952982
-
Discovery of low-molecular weight anti-PD-L1 peptides for cancer immunotherapy.J Immunother Cancer. 2019 Oct 22;7(1):270. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0705-y. J Immunother Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31640814 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Tumor Potential of Post-Translational Modifications of PD-1.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Mar 6;46(3):2119-2132. doi: 10.3390/cimb46030136. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38534752 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Not-So-Ancient Grease History: Click Chemistry and Protein Lipid Modifications.Chem Rev. 2021 Jun 23;121(12):7178-7248. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c01108. Epub 2021 Apr 6. Chem Rev. 2021. PMID: 33821625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Programmed death ligand 1 signals in cancer cells.Nat Rev Cancer. 2022 Mar;22(3):174-189. doi: 10.1038/s41568-021-00431-4. Epub 2022 Jan 14. Nat Rev Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35031777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein cysteine palmitoylation in immunity and inflammation.FEBS J. 2021 Dec;288(24):7043-7059. doi: 10.1111/febs.15728. Epub 2021 Feb 12. FEBS J. 2021. PMID: 33506611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-translational Modification of PD-1: Potential Targets for Cancer Immunotherapy.Cancer Res. 2024 Mar 15;84(6):800-807. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-23-2664. Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38231470 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct antibody clones detect PD-1 checkpoint expression and block PD-L1 interactions on live murine melanoma cells.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 21;12(1):12491. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16776-1. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35864188 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

