Ranking Methodology to Evaluate the Severity of a Quality Gap Using a National EHR Database
- PMID: 34457172
- PMCID: PMC8378648
Ranking Methodology to Evaluate the Severity of a Quality Gap Using a National EHR Database
Abstract
Selecting quality improvement projects can often be a reactive process. In order to demonstrate a data-driven strategy, we used multi-site, de-identified electronic health record (EHR) data to prioritize the severity of a quality concern: inappropriate A1c test orders for sickle cell disease patients in two randomly chosen facilities (Facility A & B). The best linear unbiased predictions (BLUP) generated from Generalized Linear Mixed Model (GLMM) was estimated for all 393 facilities with 37,151 SCD patients in the Cerner Health FactsTM (HF) data warehouse based on the ratio of inappropriate A1c orders. Ranking the BLUP after applying the GLMM indicates that the facility A being in the second quartile may not have a quality gap as significant as facility B in the top quartile for this quality concern. This study illustrates the utility of multisite EHR data for evaluating QI projects and the utility of GLMM to enable this analysis.
©2021 AMIA - All rights reserved.
Figures
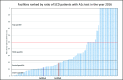
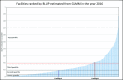
Similar articles
-
Use of large scale EHR data to evaluate A1c utilization among sickle cell disease patients.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2021 Sep 18;21(1):268. doi: 10.1186/s12911-021-01632-5. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2021. PMID: 34537047 Free PMC article.
-
A privacy-preserving and computation-efficient federated algorithm for generalized linear mixed models to analyze correlated electronic health records data.PLoS One. 2023 Jan 17;18(1):e0280192. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0280192. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36649349 Free PMC article.
-
Creation and Use of an Electronic Health Record Reporting Database to Improve a Laboratory Test Utilization Program.Appl Clin Inform. 2018 Jul;9(3):519-527. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1666843. Epub 2018 Jul 11. Appl Clin Inform. 2018. PMID: 29998456 Free PMC article.
-
Recommendations for the Conduct and Reporting of Research Involving Flexible Electronic Health Record-Based Interventions.Ann Intern Med. 2020 Jun 2;172(11 Suppl):S110-S115. doi: 10.7326/M19-0880. Ann Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 32479179 Review.
-
Making electronic health records support quality management: A narrative review.Int J Med Inform. 2017 Aug;104:105-119. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2017.03.003. Epub 2017 Mar 9. Int J Med Inform. 2017. PMID: 28599812 Review.
Cited by
-
Standardized Health data and Research Exchange (SHaRE): promoting a learning health system.JAMIA Open. 2022 Jan 17;5(1):ooab120. doi: 10.1093/jamiaopen/ooab120. eCollection 2022 Apr. JAMIA Open. 2022. PMID: 35047761 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lohr KN. Vol. 1. National Academies Press; 1990. Medicare: a strategy for quality assurance. - PubMed
-
- Plebani M, Sciacovelli L, Marinova M, Marcuccitti J, Chiozza ML. Quality indicators in laboratory medicine: a fundamental tool for quality and patient safety. Clin Biochem. 2013;46(13–14):1170–4. - PubMed
-
- Medicare C for, Baltimore MS 7500 SB. Usa M. Overview [Internet] 2018. [cited 2019 Jan 30]. Available from: https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Quality-Initiatives-Patient-Assessment-Inst... .
-
- NQF: Improving Healthcare Quality [Internet] [cited 2019 Jan 30]. Available from: https://www.qualityforum.org/Setting_Priorities/Improving_Healthcare_Qua... .
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
